Delta Centauri (δ Cen) is a massive, hot blue star located 410 light years away in the southern constellation of Centaurus. With an apparent magnitude of 2.57, it is the eighth brightest star in Centaurus. The variable star is informally known as Ma Wei. It appears near the Southern Cross, one of the most familiar asterisms in the southern celestial hemisphere.
Star type
Delta Centauri is a massive blue main sequence star of the spectral type B2Vne. Older sources classify the star as a subgiant with the stellar classification B2 IVne. The suffix “n” indicates broad absorption lines in the star’s spectrum, while the “e” means that Delta Centauri is a Be star. Be stars are non-supergiant B-type stars that show emission lines, caused by a circumstellar gaseous disk of material expelled from the stars because of their fast spin rate.
The star has a mass of 8.7 solar masses and a radius 8.18 times that of the Sun. With an effective temperature of 22,150 K, it is 5,129 times more luminous than the Sun. It has an estimated age of around 21.5 million years.
Delta Centauri is an exceptionally fast spinner, with a projected rotational velocity of 263 km/s. Because of its fast rotation, the star has an oblate shape. It is flattened at the poles and has an equatorial bulge.
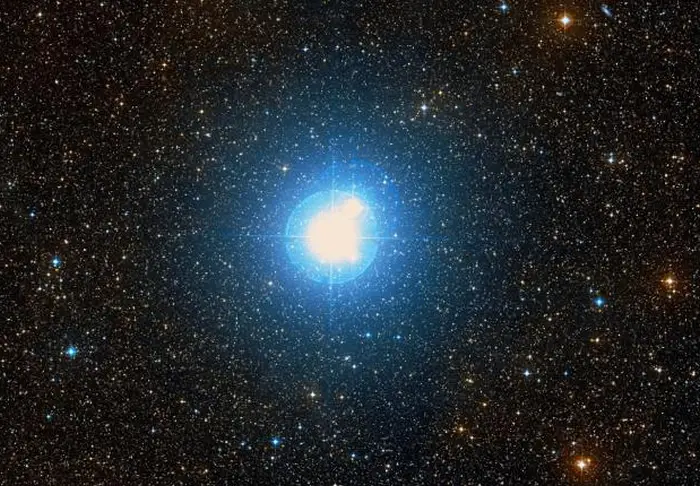

Delta Centauri, image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Like all fast spinners, Delta Centauri is an example of gravity darkening. Because its poles are closer to the centre of mass, they are hotter and brighter than the equatorial region. In other words, they are gravity brightened, while the equator is gravity darkened. The gravity darkening is the reason for the disparity in the star’s spectral classification. In 1979, Delta Centauri was classified as a subgiant star, one that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen it its core and begun to evolve away from the main sequence. More recent sources classify it as a main sequence star.
The fast spin rate is also responsible for an equatorial disk of material expelled from the star. Delta Centauri is a shell star, a star that shows broad absorption lines due to the rapid rotation and some emission lines from the equatorial disk. The presence of circumstellar gas produces an excess emission in the infrared.
Delta Centauri is also classified as a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable. The star’s brightness varies from magnitude 2.51 to 2.56. Gamma Cassiopeiae stars show brightness variations because they have equatorial decretion disks which occasionally disappear or reform. They are hot stars that spin very rapidly. Bright examples of the class include the prototype Gamma Cassiopeiae in the constellation Cassiopeia, Dschubba (Delta Scorpii) in Scorpius, Kappa Canis Majoris in Canis Major, Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris) in Canis Minor, Zeta Ophiuchi in Ophiuchus, Pleione (28 Tauri) in the Pleiades cluster (Messier 45) in Taurus, and Lambda Pavonis in Pavo.
Some variations in brightness may be explained by the presence of an unseen companion. If Delta Centauri is a binary star, the companion would need to be 4-7 times more massive than the Sun and lie at least 6.9 astronomical units away, and the system would need to have an orbital period of at least 4.6 years.
Delta Centauri has a common proper motion with the fainter stars HD 105382 and HD 105383. The three stars may form a triple star system or be members of a small cluster. HD 105382 is classified as a main sequence star of the spectral type B5V. It lies at a separation of 267 arcseconds from Delta Centauri and is located at a distance of 440 light-years. HD 105383 has the stellar classification B9V, indicating a blue main sequence star.
Facts
Shining at magnitude 2.57, Delta Centauri is the eighth brightest point of light in Centaurus and, on average, the 100th brightest star in the night sky. It is only slightly fainter than Leepwal (Zeta Centauri) in the constellation Centaurus, Zosma (Delta Leonis) in Leo, and Acrab (Beta Scorpii) in Scorpius. It is about as bright as Arneb (Alpha Leporis) in Lepus, and just outshines Gienah (Gamma Corvi) in Corvus, Ascella (Zeta Sagittarii) in Sagittarius, Zubeneschamali (Beta Librae) in Libra, and Unukalhai (Alpha Serpentis) in Serpens.
Without extinction caused by intervening dust, Delta Centauri would have an apparent visual magnitude of 2.22 and rival Gamma Centauri as the fourth brightest star in Centaurus.
Delta Centauri is a member of the Lower Centaurus-Crux subgroup of the larger Scorpius-Centaurus OB association (Sco OB2). The Scorpius-Centaurus association is the nearest association of massive O- and B-type stars to the Sun. Other bright members of Sco OB2 include Antares in the constellation Scorpius, Acrux and Mimosa in Crux, Zeta Ophiuchi in Ophiuchus, and Hadar in Centaurus.
The people of Luritja and Aranda in Central Australia consider Delta Centauri part of Iritjinga, the Eagle-Hawk. The quadrangular asterism is formed by Delta Centauri with Gamma Centauri, Gacrux (Gamma Crucis), and Imai (Delta Crucis).
Name
Delta Centauri does not have a proper name formally approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is one of the brightest stars without a formal name, along with Gamma Velorum (popularly known as Regor), Gamma Cassiopeiae (Navi), Gamma Centauri (Muhlifain), Epsilon Centauri, Eta Centauri, Kappa Scorpii (Girtab), and Zeta Ophiuchi (Han).
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Delta Centauri was known as 馬尾三 (Mǎ Wěi sān), the Third Star of Horse’s Tail. It formed the Horse’s Tail asterism with the fainter G Centauri and Rho Centauri. The asterism was introduced in the early 17th century, after the arrival of western star charts. The star’s Chinese name has led to the name Ma Wei, which is sometimes used for the star.
Location
Delta Centauri lies in the same region of the sky as the Southern Cross, formed by the brightest stars of the constellation Crux. The star can be found by extending a line from Mimosa (Beta Crucis) through Gacrux (Gamma Crucis). Its brighter neighbour Gamma Centauri appears along the line drawn through the long axis of the Southern Cross, from Acrux (Alpha Crucis) through Gacrux (Gamma Crucis).
At declination -50° 43′, Delta Centauri is best seen from the southern hemisphere. It never rises above the horizon for observers north of the latitude 39° N.
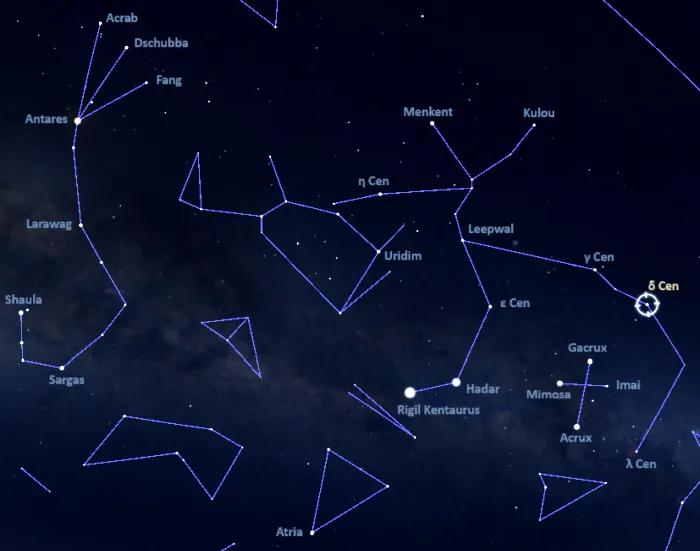
Location of Delta Centauri, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Delta Centauri is located in the southern constellation of Centaurus. The celestial Centaur is one of the ancient constellations catalogued by Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. It is one of the brightest constellations in the sky, as well as one of the largest. Occupying an area of 1,060 square degrees, it is the ninth largest of the 88 modern constellations.
Centaurus is well known for its bright stars and deep sky objects. It hosts Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar (Alpha and Beta Centauri), the third and 11th brightest stars in the sky. Proxima Centauri (Alpha Centauri C), the faintest component of the Alpha Centauri system, is the nearest individual star to the Sun. It lies only 4.2465 light-years away.
Other notable stars in Centaurus include the K-type giant Menkent (Theta Centauri), the hot blue subgiant star Leepwal (Zeta Centauri), the double star Gamma Centauri, the blue B-type stars Eta Centauri and Epsilon Centauri, and the A-type main sequence star Kulou (Iota Centauri).
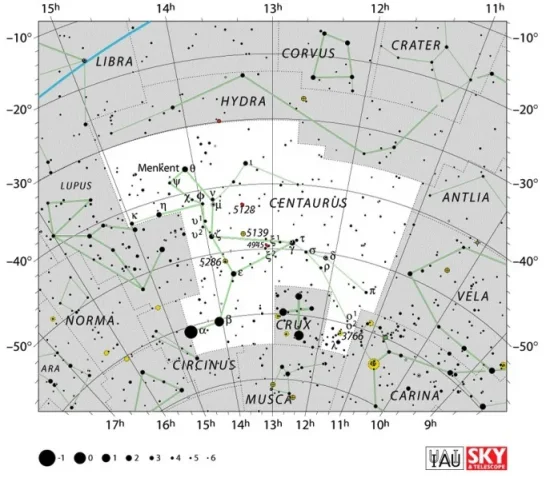
Centaurus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Centaurus is also home to the Mira variable R Centauri, the white dwarf known as Lucy or the Diamond Star, the chemically peculiar Przybylski’s Star, and the hypergiant V766 Centauri, one of the largest stars known.
Deep sky objects in the constellation include the bright, large globular cluster Omega Centauri (NGC 5139), the Pearl Cluster (NGC 3766), the active galaxy Centaurus A (NGC 5128), the Backward Galaxy (NGC 4622), the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4945, the blue dwarf galaxy NGC 5253, the Lambda Centauri Nebula (IC 2944), the protoplanetary Boomerang Nebula, and the Blue Planetary Nebula (NGC 3918), also known as the Southerner.
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects of Centaurus is during the month of May, when the constellation climbs higher above the horizon in the early evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations south of the latitude 25° S. From the southern hemisphere, Centaurus can be seen throughout the year.
The 10 brightest stars in Centaurus are Alpha Centauri (mag. -0.27), Hadar (Beta Cen, mag. 0.61), Menkent (Theta Cen, mag. 2.06), Gamma Centauri (mag. 2.17), Epsilon Centauri (mag. 2.30), Eta Centauri (mag. 2.35), Leepwal (Zeta Cen, mag. 2.55), Delta Centauri (mag. 2.57), Kulou (Iota Cen, mag. 2.73), and Lambda Centauri (mag. 3.13).
Delta Centauri
| Spectral class | B2Vne or B2 IVne |
| Variable type | Gamma Cassiopeiae (γ Cas) |
| U-B colour index | −0.92 |
| B-V colour index | −0.13 |
| Apparent magnitude | 2.57 (2.51 – 2.65) |
| Absolute magnitude | −2.94 |
| Distance | 410 ± 20 light-years (127 ± 8 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 5.7179 ± 0.6516 mas |
| Radial velocity | +11 ± 4 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: -42.613 ± 0.413 mas/yr |
| Dec.: −11.135 ± 0.482 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 8.7 ± 0.3 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 5,129 L☉ |
| Radius | 8.18 ± 0.16 R☉ |
| Temperature | 22,150 ± 222 K |
| Age | 21.5 ± 1.5 million years |
| Rotational velocity | 263 ± 14 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 3.43 ± 0.03 cgs |
| Constellation | Centaurus |
| Right ascension | 12h 08m 21.4976373s |
| Declination | −50° 43′ 20.738614″ |
| Names and designations | Ma Wei, Delta Centauri, Delta Cen, δ Centauri, δ Cen, HD 105435, HR 4621, HIP 59196, SAO 239689, FK5 452, PPM 340720, CD−50°6697, CPD−50°4862, CPC 0 10112, PLX 2794.10, GC 16584, GCRV 7275, SKY# 22784, HGAM 2006, ALS 14963, CSV 6892, Hen 3-753, JP11 2167, EM* MWC 219, N30 2812, GEN# +1.00105435, SACS 264, ROT 1783, GSC 08241-03235, UBV 10892, UBV M 17783, uvby98 100105435, WEB 10531, AAVSO 1203-50, IRAS 12057-5026, 2MASS J12082152-5043208, TD1 16088, TIC 333670784, TYC 8241-3235-1, Gaia DR3 6126469654585981952, CCDM J12083-5043A, IDS 12032-5010 A, WDS J12084-5043A |