Homam, Zeta Pegasi (ζ Peg), is a hot blue main sequence star located approximately 204 light-years away in the constellation Pegasus. With an apparent magnitude of 3.414, it is the sixth brightest star in Pegasus. It appears in the southern part of the constellation, in the neck of Pegasus.
Star type
Homam is a massive blue main sequence star of the spectral type B8 V. It has a mass 3.22 times that of the Sun and a radius 4.23 times the Sun’s. With a surface temperature of 12,300 K, it is 224 times more luminous than the Sun. The star has an estimated age of only 120 million years.
Zeta Pegasi is a very fast spinner. It has a projected rotational velocity between 140 and 210 km/s and takes less than 1.4 days to complete a rotation. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of 9.23 km/s. Even though it is a young star, Homam is not known to be part any star cluster or stellar moving group.
Zeta Pegasi is classified as a slowly pulsating B star (SPB). Slowly pulsating B-type stars are pulsating variable stars whose brightness varies by less than 0.1 magnitudes with periods between half a day and five days. They show variability both in brightness and spectral line profile. Other examples of this class include the brighter Algenib in Pegasus, Omicron Velorum in Vela, Iota Herculis and Tau Herculis in Hercules, Gamma Muscae in Musca, Rho Lupi in Lupus, and Nu Eridani in Eridanus. Some of these stars are also classified as Beta Cephei variables.
The brightness of Homam varies with a period of 22.952 ± 0.804 hours.
Homam has two visual companions. One appears at a separation of 68 seconds of arc and shines at magnitude 11.6, and the other is an 11th magnitude star separated by 177 arcseconds from Homam.
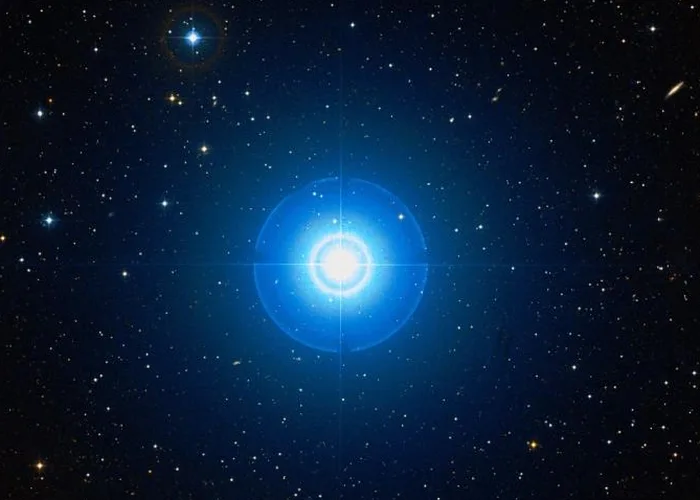

Homam (Zeta Pegasi), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Facts
With an apparent magnitude of 3.414, Homam is, on average, the 263rd brightest star in the night sky. It is only slightly fainter than Lambda Tauri in the constellation Taurus, Heng (Nu Centauri) in Centaurus, and Zeta Lupi in Lupus. It is about as bright as Eta Cephei in Cepheus, and it just outshines Mothallah (Alpha Trianguli) in Triangulum, Eta Lupi in Lupus, Mu Herculis in Hercules, and Beta Pavonis in Pavo.
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Zeta Pegasi was known as 雷電一 (Léi Diàn yī), the First Star of Thunder and Lightning. It formed an asterism called Thunder and Lightning with the fainter Xi Pegasi, Sigma Pegasi, 55 Pegasi, 66 Pegasi, and 70 Pegasi. The asterism was part of the larger Encampment mansion, one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise.
Name
The traditional name Homam (pronunciation: /ˈhoʊmæm/) means “man of high spirit” or “the high-minded man” in Arabic. It is derived from the phrase sa’d al-humam, “the lucky stars of the hero” or “the lucky stars of the high-minded man.” The name originally applied to Zeta and Xi Pegasi. It was sometimes spelled Homan.
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) approved the name Homam for Zeta Pegasi on August 21, 2016.
The 16th century Arabic astronomer Al Tizini called Zeta Pegasi Sa’d al Naamah, the Lucky Star of the Ostriches, and the 17th century Egyptian astronomer Al Achsasi al Mouakket called it Na’ir Sad al Bahaim, meaning the Bright Fortunate One of the Two Beasts.
Location
Homam is very easy to find because it appears in the same area as the Great Square of Pegasus, a prominent asterism formed by Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae) in the constellation Andromeda with Scheat (Beta Pegasi), Markab (Alpha Pegasi) and Algenib (Gamma Pegasi) in Pegasus.
Homam appears southwest of Markab at the southwestern vertex of the Great Square. The fainter Xi Pegasi (mag. 4.195) appears between Homam and Markab. The spiral galaxy NGC 7347 lies in the same field of view as Homam.
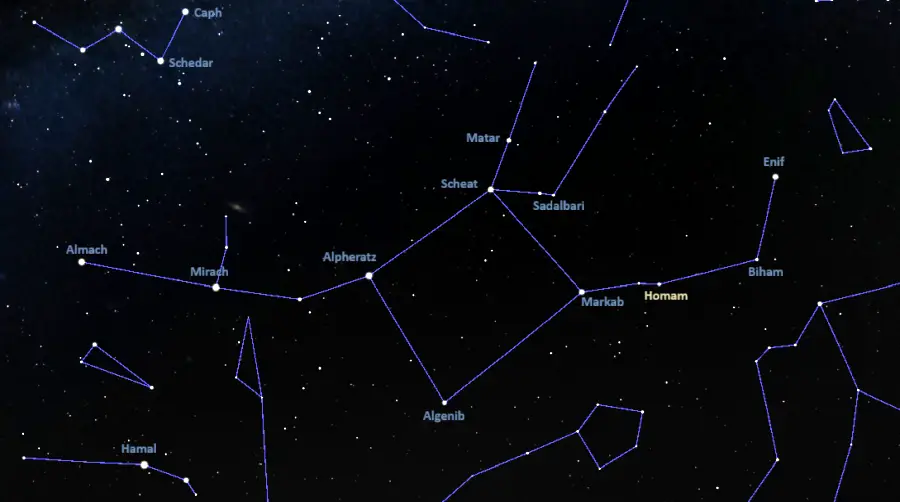
Homam location, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Homam is located in the constellation of Pegasus. Pegasus stretches across 1,121 square degrees of the sky just north of the celestial equator and is the seventh largest of the 88 modern constellations. It is one of the 48 Greek constellations, catalogued by the Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century AD. In Greek mythology, the constellation is associated with the winged horse Pegasus, the offspring of the Gorgon Medusa and the sea god Poseidon.
Pegasus is one of the most prominent northern constellations. Its bright stars Markab, Scheat and Algenib form the Great Square of Pegasus with Alpheratz in Andromeda. The asterism dominates the autumn sky in the northern hemisphere.
Enif (Epsilon Pegasi), the brightest star in Pegasus, is an orange supergiant that shines at magnitude 2.399 from a distance of 690 light-years from the solar system. The massive supernova candidate marks the nose of Pegasus.
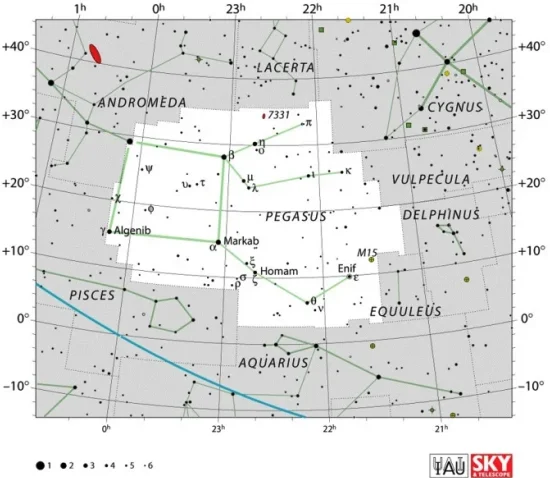
Pegasus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Other notable stars in the constellation include the massive blue star Algenib (Gamma Pegasi), the red giant or bright giant Scheat (Beta Pegasi), the yellow giant or bright giant Lambda Pegasi, the white subgiant Markab (Alpha Pegasi), the yellow giant Sadalbari (Mu Pegasi), the yellow bright giant Matar (Eta Pegasi), the yellow-white giant Alkarab (Upsilon Pegasi), and the fast-spinning A-type star Biham (Theta Pegasi).
Pegasus also contains the yellow supergiant 9 Pegasi, the orange supergiant 12 Pegasi, the chemically peculiar star Salm (Tau Pegasi), IK Pegasi, one of the nearest supernova candidates to the Sun, and the Sun-like star 51 Pegasi (Helvetios), the first main sequence star discovered to have an orbiting extrasolar planet (51 Pegasi b).
Deep sky objects in the constellation include the Great Pegasus Cluster (M15), a bright globular cluster listed in the Messier catalogue, the spiral galaxy NGC 7331 with the Deer Lick Group, the Fried Egg Galaxy (NGC 7742), the spiral galaxy NGC 7217, the Superman Galaxy (NGC 7479), and the interacting pairs NGC 7469 and IC 5283 and NGC 7752 and NGC 7753.
Pegasus also hosts the gravitationally lensed quasar known as the Einstein Cross and the famous Stephan’s Quintet, a visual grouping of five galaxies, four of which are in the process of interacting.
The best time of the year to see the stars and deep sky objects in Pegasus is during the month of October, when the constellation climbs higher above the horizon in the early evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations north of the latitude 60° S.
The 10 brightest stars in Pegasus are Enif (Epsilon Peg, mag. 2.399), Scheat (Beta Peg, mag. 2.42), Markab (Alpha Peg, mag. 2.48), Algenib (Gamma Peg, mag. 2.84), Matar (Eta Peg, mag. 2.95), Homam (Zeta Peg, mag. 3.414), Sadalbari (Mu Peg, mag. 3.514), Biham (Theta Peg, mag. 3.52), Iota Pegasi (mag. 3.77), and Lambda Pegasi (mag. 3.93).
Homam – Zeta Pegasi
| Spectral class | B8 V |
| Variable type | Slowly pulsating B-type star (SPB) |
| U-B colour index | -0.181 |
| B-V colour index | -0.088 |
| Apparent magnitude | +3.414 |
| Distance | 204 ± 2 light years (62.7 ± 0.7 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 15.96 ± 0.19 mas |
| Radial velocity | +9.23 ± 0.38 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: +77.22 ± 0.17 mas/yr |
| Dec.: −11.38 ± 0.15 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 3.22 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 224 L☉ |
| Radius | 4.23 ± 0.25 R☉ |
| Temperature | 12,300 ± 1,000 K |
| Metallicity | +0.06 dex |
| Age | 120 million years |
| Rotational velocity | 140 – 210 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 3.67 ± 0.05 cgs |
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Right ascension | 22h 41m 27.7207176s |
| Declination | +10° 49′ 52.907917″ |
| Names and designations | Homam, Zeta Pegasi, Zeta Peg, ζ Pegasi, ζ Peg, 42 Pegasi, 42 Peg, HD 214923, HR 8634, HIP 112029, SAO 108103, FK5 855, BD+10 4797, AG+10 3107, GC 31664, GCRV 14247, N30 4992, CSI+10 4797 1, PLX 5492.00, PPM 141743, SKY# 43140, GEN# +1.00214923, JP11 3523, GSC 01155-02187, PMC 90-93 602, SRS 30855, AKARI-IRC-V1 J2241277+104952, ROT 3307, TD1 29271, TIC 322187270, YZ 10 9059, UCAC3 202-315734, uvby98 100214923, WEB 19999, WISE J224127.76+104952.7, UBV 19416, UBV M 26553, TYC 1155-2187-1, IRAS 22389+1034, 2MASS J22412773+1049526, Gaia DR2 2717594072113581696, Gaia DR3 2717594072113956352, ADS 16182 A, CCDM J22415+1050A, IDS 22365+1019 A, WDS J22415+1050A |