Dabih (Beta Capricorni Aa) is the primary component in a multiple star system located approximately 390 light years away in the zodiac constellation Capricornus. With an apparent magnitude of 3.05, it is the second brightest star in Capricornus, after Deneb Algedi. It appears in the head of the Sea Goat.
Star system
The Beta Capricorni system is composed of five stars. It appears as a visual binary star through binoculars and small telescopes. The two visual components are designated Beta1 Capricorni and Beta2 Capricorni.
The brighter Beta1 Capricorni shines at magnitude 3.05 and Beta2 Capricorni has an apparent magnitude of 6.09. Beta1 and Beta2 are separated by 3.5 arcminutes in the sky, corresponding to a physical distance of at least 0.34 light-years (21,000 astronomical units). If they are gravitationally bound, they have an orbital period of around a million years.
Each component of the visual binary pair is composed of multiple stars. Beta1 Capricorni consists of three components: Dabih (Beta Capricorni Aa) and the binary pair Beta Capricorni Ab, composed of Beta Capricorni Ab1 and Beta Capricorni Ab2.
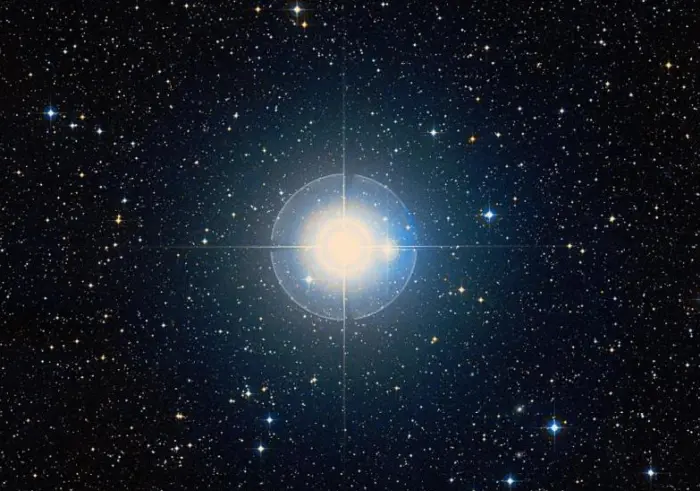

Dabih (Beta Capricorni), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
The components Beta Capricorni Aa and Ab orbit each other with a period of 3.762 years and are separated by 0.049 arcseconds in the sky, corresponding to a physical separation of 5 astronomical units (Earth – Sun distances). The binary pair Beta Capricorni Ab1 and Ab2 have an orbital period of 8.677 days and an orbital distance of only 0.1 AU.
The components of Beta1 Capricorni have the spectral classes K0II (Beta Cap Aa), indicating an orange bright giant, and B8V (Beta Cap Ab1), indicating a blue main sequence star.
Beta Capricorni Aa has a mass of 3.69 solar masses and a radius 31.4 times that of the Sun. With an effective temperature of 4,870 K, it shines with 501 solar luminosities.
The component Beta Capricorni Ab1 is more massive and luminous. It has a mass 4.22 times that of the Sun and shines with a luminosity of 112 Suns. Its close neighbour Beta Capricorni Ab2 has 94% of the Sun’s mass. All three components have an estimated age of 230 million years.
Beta2 Capricorni is a binary system consisting of Beta Capricorni Ba and Beta Capricorni Bb. The two components orbit each other with a period of 400 years and are separated by 0.689 seconds of arc. They form a single-lined spectroscopic binary star. This means that the spectrum of only one of the two stars is visible. The presence of the secondary component can be inferred from the primary component’s spectral lines periodically shifting towards the blue and then towards red.
Beta Capricorni Ba has the spectral type A0III. It is a main sequence star that presents as a white giant. The star has a mass 2.53 times that of the Sun and a radius of 1.98 solar radii. With a surface temperature of 11,188 K, it is 55 times more luminous than the Sun. It is a mercury-manganese star, a chemically peculiar star with strong spectral lines of mercury and manganese.
The companion, Beta Capricorni Bb, has 1.23 times the Sun’s mass.
The Beta Capricorni system has two other visual companions, sometimes called Beta Capricorni D and E. However, it is unclear whether these stars are physically related to the Dabih system or simply appear in the same line of sight.

Beta1 and Beta2 Capricorni, image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Facts
With an apparent magnitude of 3.05, Dabih is the second brightest star in the constellation Capricornus and, on average, the 148th brightest star in the sky. It is only slightly fainter than Minkar (Epsilon Corvi) in the constellation Corvus, Almaaz (Epsilon Aurigae) in Auriga, and Seginus (Gamma Boötis) in Boötes. It is about as bright as Beta Muscae in Musca, Mebsuta (Epsilon Geminorum) in Gemini, and Tania Australis (Mu Ursae Majoris) in Ursa Major, and it just outshines Altais (Delta Draconis) in Draco, Eta Sagittarii in Sagittarius, and Zeta Hydrae in Hydra.
The Beta Capricorni star system is moving towards the Sun with a radial velocity of -19 km/s.
Dabih lies close to the ecliptic and can sometimes be occulted by the Moon. It can also be occulted by planets, but this happens very rarely.
Name
The name Dabih (pronunciation: /ˈdeɪbiː/) comes from the Arabic al-dhābiḥ, meaning “the butcher.” Beta Capricorni was historically also called Dahib, Dabikh and Dikhabda. The name and its variations come from the phrase Sa’d adh-dhabih, meaning “the lucky star of the slaughterer.” The name once referred to an Arabic lunar mansion formed by Dabih with Algedi (Alpha2 Capricorni) and Alpha1 Capricorni.
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) officially approved the name Dabih for Beta Capricorni Aa on August 21, 2016. The name formally applies only to the primary component but has traditionally been used for the whole star system. The components Beta1 and Beta2 Capricorni were historically called Dabih Major and Dabih Minor.
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Beta Capricorni was known as 牛宿一 (Niú Su yī), the First Star of Ox. It formed the Ox asterism with Algedi (Alpha2 Capricorni), Xi2 Capricorni, Pi Capricorni, Omicron Capricorni, and Rho Capricorni. The asterism was part of the larger Ox mansion, one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise.
Location
Dabih is not difficult to find. While its host constellation does not stand out in the sky, the V-shaped constellation figure of the Sea Goat can be made out on a clear night from areas without too much light pollution.
Dabih and the fainter Algedi (Alpha2 Capricorni) can be found using the bright stars of the neighbouring constellation Aquila. Altair, the brightest star in Aquila and the 12th brightest star in the sky, forms an asterism known as the Shaft of Aquila (or Family of Aquila) with the fainter Tarazed and Alshain. A line extended through the asterism leads to the right side of the V-shaped figure of Capricornus. Algedi is the first relatively bright star along the line and the brighter Dabih is the second.
At declination – 14° 47′, Beta Capricorni is visible from virtually any location for at least part of the year.

Location of Dabih (Beta Capricorni), image: Stellarium
Constellation
Dabih is located in the constellation Capricornus. The celestial Sea Goat is one of the Greek constellations, catalogued by the astronomer Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, the constellation is associated with the goat Amalthea, who nursed the infant Zeus. Alternatively, it is taken to represent the forest deity Pan. Like all zodiac constellations, Capricornus lies on the ecliptic (the Sun’s apparent path across the sky) and is invisible for about a month when the Sun appears to pass through it.
Capricornus is the 40th largest constellation in the sky. It stretches across 414 square degrees of the southern sky between Sagittarius, Aquila, Aquarius, Piscis Austrinus, and Microscopium.
The Sea Goat constellation is relatively inconspicuous. Its brightest star, the white giant Deneb Algedi (Delta Capricorni Aa), shines at magnitude 2.81 from a distance of 38.70 light years. It is the only star in the constellation that is brighter than magnitude 3.0.
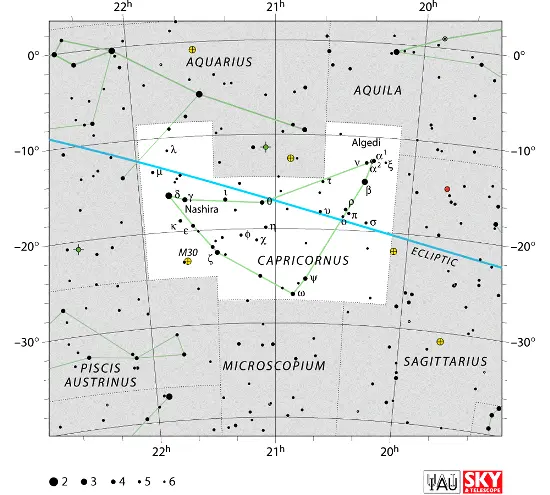
Capricornus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Other notable stars in Capricornus include the yellow bright giant or giant star Algedi (Alpha2 Capricorni), the yellow supergiants Alpha1 Capricorni (Algiedi Prima) and Zeta Capricorni, the chemically peculiar Am star Nashira (Gamma Capricorni), the hot blue star Alshat (Nu Capricorni), the A-type main sequence star Theta Capricorni, the orange giant Omega Capricorni, the F-type dwarf Psi Capricorni, the yellow giants Iota Capricorni and Kappa Capricorni, and the solar twin HD 197027.
Deep sky objects in Capricornus include the globular clusters Messier 30 and Palomar 12, the spiral galaxies NGC 6907, NGC 7019 and IC 1337, the elliptical galaxy NGC 7016, the compact galaxy group HCG 87, and the interacting lenticular galaxies NGC 7035 and NGC 7035A.
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects in Capricornus is during the month of September, when the constellation appears higher above the horizon in the early evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations south of the latitude 60° N.
The 10 brightest stars in Capricornus are Deneb Algedi (Delta Cap, mag. 2.81), Dabih (Beta Cap, mag. 3.05), Algedi (Alpha2 Cap, mag. 3.57), Nashira (Gamma Cap, mag. 3.67), Zeta Capricorni (mag. 3.77), Theta Capricorni (mag. 4.07), Omega Capricorni (mag. 4.11), Psi Capricorni (mag. 4.13), Iota Capricorni (mag. 4.296), and Alpha1 Capricorni (mag. 4.27).
Dabih – Beta Capricorni
| Apparent magnitude | +3.05 / +6.09 |
| Absolute magnitude | -2.03/+1.03 |
| Distance | 390 ± 30 light-years (119 ± 9 parsecs) |
| Constellation | Capricornus |
| Names and designations | Dabih, Dabikh, Dikhabda, Beta Capricorni, Beta Cap, β Capricorni, β Cap, 9 Capricorni, 9 Cap, FK5 762, CCDM J20210-1447, WDS J20210-1447AB |
Beta1 Capricorni
| Spectral class | K0II + B8V |
| U-B colour index | +0.27 |
| B-V colour index | +0.79 |
| Apparent magnitude | 3.05 |
| Absolute magnitude | -2.03 |
| Parallax | 8.3966 ± 0.6348 mas |
| Radial velocity | −19.0 ± 0.6 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: +44.133 ± 0.609 mas/yr |
| Dec.: +0.360 ± 0.407 mas/yr | |
| Right ascension | 20h 21m 0.6667s |
| Declination | −14° 46′ 53.067″ |
| Names and designations | Dabih, Dabih Major, Beta1 Capricorni, Beta1 Cap, β1 Capricorni, β1 Cap, 9 Capricorni, 9 Cap, HD 193495, HR 7776, HIP 100345, SAO 163481, BD−15°5629, FK5 762, GC 28295, GCRV 12703, PPM 237293, JP11 3227, IRC -10537, PLX 4845.00, STFA 52A, BLA 7, SKY# 38436, NSV 25105, SBC7 801, SBC7 802, SBC9 1224, GEN# +1.00193495, RAFGL 2555, ROT 2964, PMC 90-93 539, PMSC 20154-1506Aabc, N30 4498, UBV 17611, IRAS 20182-1456, WEB 18102, WEB 18103, YZ 104 7653, TIC 114746467, TYC 5753-2281-1, Gaia DR2 6875990375998568192, Gaia DR3 6875990375999580544, 2MASS J20210066-1446531, CCDM J20210-1447A, WDS J20210-1447A, WDS J20210-1447Aa,Ab |
Beta1 Capricorni Aa
| Mass | 3.69 ± 0.20 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 501 L☉ |
| Radius | 31.4 R☉ |
| Temperature | 4,870 K |
| Age | 230 million years |
Beta1 Capricorni Ab1
| Mass | 4.22 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 112 L☉ |
| Age | 230 million years |
Beta Capricorni Ab2
| Mass | 0.94 M☉ |
| Age | 230 million years |
Beta2 Capricorni
| Spectral class | A0III |
| U-B colour index | -0.11 |
| B-V colour index | -0.02 |
| Apparent magnitude | 6.09 |
| Absolute magnitude | +1.03 |
| Parallax | 9.8983 ± 0.3071 mas |
| Radial velocity | -17.60 ± 1.8 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: +44.411 ± 0.305 |
| Dec.: -0.637 ± 0.151 mas/yr | |
| Right ascension | 20h 20m 46.5479s |
| Declination | −14° 47′ 05.604″ |
| Names and designations | Dabih Minor, Beta2 Capricorni, Beta2 Cap, β2 Capricorni, β2 Cap, HD 193452, HR 7775, HIP 100325, SAO 163471, BD−15°5626, GC 28286, GCRV 70871, PPM 237281, SKY# 38425, BAR 12, Renson 54010, GEN# +1.00193452, SBC9 1223, PMC 90-93 6268, STF 4052B, 2MASS J20204654-1447053, uvby98 100193452, WEB 18095, UBV 17604, UBV M 24734, YZ 104 7647, TIC 114721100, TYC 5753-2282-1, Gaia DR2 6875990891389558400, Gaia DR3 6875990891389558400, CCDM J20210-1447B, WDS J20210-1447B, WDS J20210-1447Ba,Bb |
Beta Capricorni Ba
| Mass | 2.53 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 55 L☉ |
| Radius | 1.98 R☉ |
| Temperature | 11,188 K |
| Age | 230 million years |
| Surface gravity | 4.18 cgs |
Beta Capricorni Bb
| Mass | 1.23 M☉ |
| Age | 230 million years |