Algedi, Alpha2 Capricorni (α2 Cap), is a triple star system located approximately 102 light-years away in the constellation Capricornus. With an apparent magnitude of 3.57, it is the third brightest point of light in Capricornus, after Deneb Algedi and Dabih. Algedi forms a visual double star with the fainter Alpha1 Capricorni. The line-of-sight companions mark the right horn of the celestial Goat.
Star system
The Alpha2 Capricorni star system is composed of a yellow giant or subgiant star of the spectral type G8.5III-IV and a binary system consisting of two stars, each with about half the Sun’s mass. The binary star system orbits Algedi with a period of around 1,500 years. It is separated by about 6.6 arcseconds from the primary star. The secondary stars have an orbital period of 244 years.
The primary component, formally known as Algedi, is an evolved star on the red giant branch. It has a mass 2.05 times that of the Sun and a radius of 8.38 solar radii. With a surface temperature of 5,030 K, it is 40.4 times more luminous than the Sun. The giant star spins at 2.7 km/s, slightly faster than the Sun. It has an estimated age of 1.3 billion years.
Algedi has evolved away from the main sequence and is now fusing hydrogen in a shell around an inert helium core. It is not massive enough to end its life as a supernova. Instead, when it reaches the end of its life cycle, it will cast away its outer layers to form a planetary nebula and slowly cool and fade as a white dwarf.
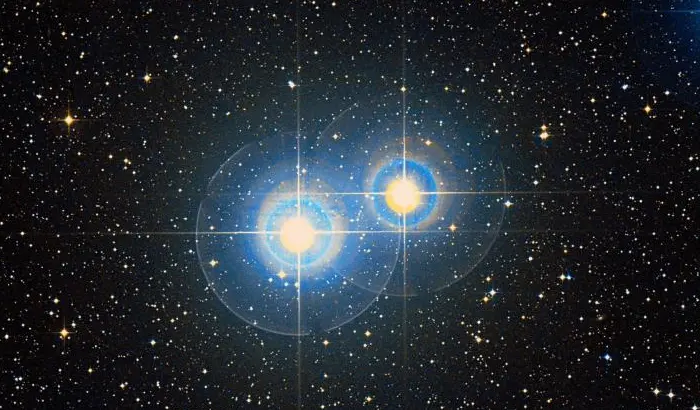

Algedi (Alpha² Capricorni), image: Wikisky
Facts
Alpha2 Capricorni and Alpha1 Capricorni appear as an optical double star, but they are not physically related. The two stars are separated by 0.11 degrees in the sky and can be resolved with the unaided eye.
The fainter Alpha1 Capricorni lies at a much greater distance from the Sun – around 870 light-years away – and is a much more massive and intrinsically luminous star. It is a yellow supergiant of the spectral type G3 Ib. It has a mass of 5.3 solar masses and a radius 36.3 times the Sun’s. With an effective temperature of 5,119 K, it is 1,047 times more luminous than the Sun. It shines at magnitude 4.27 and has a fainter (mag. 8.60) companion, discovered by the Hipparcos satellite in 2000.
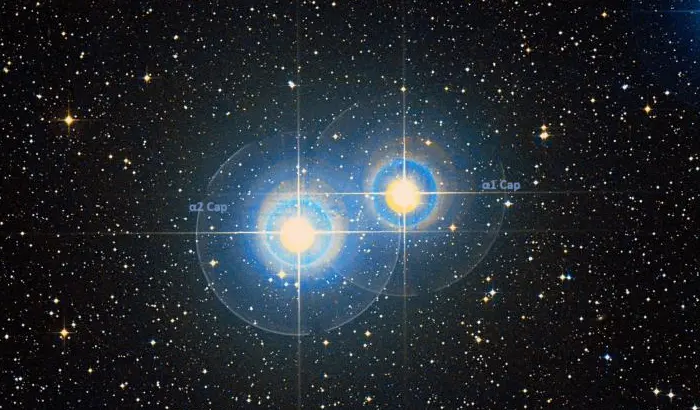

Alpha¹ Capricorni and Alpha² Capricorni, image: Wikisky
Algedi has the Bayer designation Alpha even though it is only the third brightest star in Capricornus because it is the westernmost of the stars that form the faint constellation figure of the Sea Goat. Deneb Algedi, the constellation’s brightest star, has the designation Delta Capricorni and marks the tail of the goat. It lies in the eastern part of Capricornus.
Algedi appears close to the radiant of the Alpha Capricornids, a meteor shower visible from early July to mid-August. The parent body of the meteor shower is the comet 169P/NEAT.
Name
The name Algedi (pronunciation: /ælˈdʒiːdi/) comes from the Arabic al-jadii, meaning “the goat.” It was historically also spelled Algiedi or Giedi. This was the traditional name of both points of light with the Bayer designation Alpha Capricorni. Alpha1 Capricorni was historically known as Algiedi Prima or Prima Giedi (the First Goat) and Alpha2 as Algiedi Secunda or Secunda Giedi (the Second Goat).
The name Algedi was approved by the International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) on August 21, 2016.
In Chinese astronomy, Algedi was known as 牛宿二 (Niú Xiù èr), the Second Star of Ox. The star was part of the Ox asterism, which also consisted of Dabih (Beta Capricorni), Xi2 Capricorni, Pi Capricorni, Omicron Capricorni, and Rho Capricorni. The asterism was part of the larger Ox mansion, one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise.
Location
Algedi is relatively easy to find but, shining at fourth magnitude (close to third magnitude), it does not stand out in the sky and is a challenging target from areas with a significant amount of light pollution. The star appears near the imaginary line extended from the Shaft of Aquila. The brighter Dabih (Beta Capricorni) appears along the same line.
The Shaft of Aquila (or the Family of Aquila) is formed by Altair, the 12th brightest star in the sky, and the two stars flanking it, Tarazed and Alshain. Altair is one of the stars of the Summer Triangle and the brightest star in the bird-like pattern of the constellation Aquila (the Eagle).
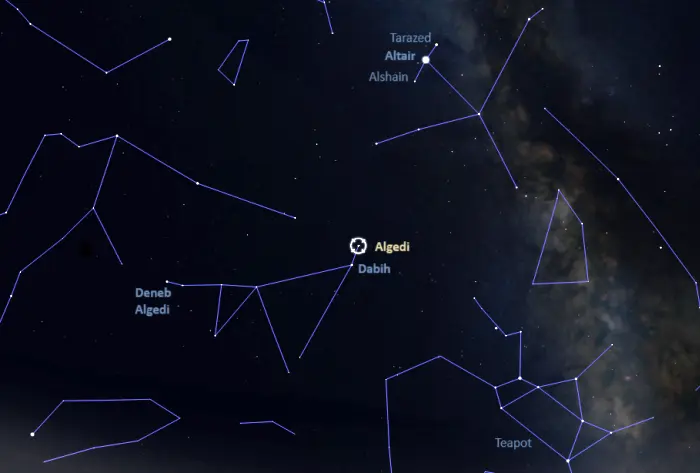
The location of Algedi, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Algedi is located in the constellation Capricornus, the Sea Goat. Capricornus is one of the 48 Greek constellations catalogued by Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, the constellation is associated with the goat Amalthea and the forest deity Pan. Like other zodiac constellations, it lies on the ecliptic, the Sun’s apparent path across the sky.
Capricornus occupies an area of 414 square degrees south of the celestial equator and is the 40th largest constellation in the sky. With only one star brighter than magnitude 3.0, it is one of the faintest zodiac constellations. Its brightest star, the white A-type giant Deneb Algedi (Delta Capricorni Aa), shines at magnitude 2.81 from a distance of 38.70 light-years. It is classified as an Algol-type eclipsing binary system.
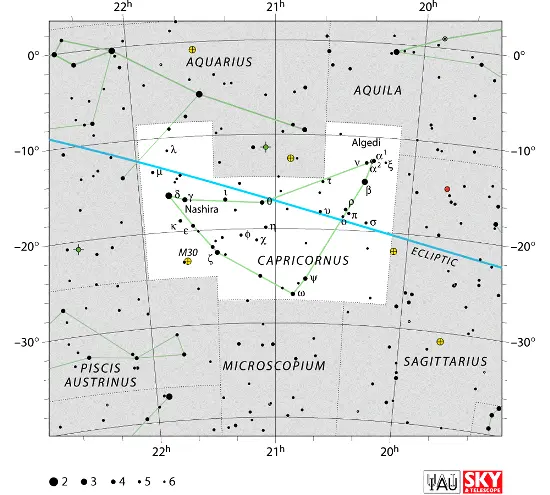
Capricornus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine
Other notable stars in Capricornus include the multiple star-system Beta Capricorni (Dabih), the chemically peculiar Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable Nashira (Gamma Capricorni), the hot blue B-type star system Pi Capricorni, the yellow supergiants Alpha1 Capricorni and Zeta Capricorni, the orange giant Omega Capricorni, and the yellow giant Iota Capricorni.
Deep sky objects in Capricornus include the globular clusters Messier 30 and Palomar 12, the compact galaxy group HCG 87, the spiral galaxies NGC 6907 and IC 1337, and the interacting pair of lenticular galaxies catalogued as NGC 7035 and NGC 7035A.
The best time of the year to see Algedi and other stars and deep sky objects in Capricornus is during the month of September, when the constellation climbs higher above the horizon in the evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations south of the latitude 60° N.
The 10 brightest stars in Capricornus are Deneb Algedi (Delta Cap, mag. 2.81), Dabih (Beta Cap, mag. 3.05), Algedi (Alpha2 Cap, mag. 3.57), Nashira (Gamma Cap, mag. 3.67), Zeta Capricorni (mag. 3.77), Theta Capricorni (mag. 4.07), Omega Capricorni (mag. 4.11), Psi Capricorni (mag. 4.13), Iota Capricorni (mag. 4.296), and Alpha1 Capricorni (mag. 4.27).
Algedi – Alpha2 Capricorni
| Spectral class | G8.5III-IV |
| U-B colour index | +0.69 |
| B-V colour index | +0.94 |
| Apparent magnitude | 3.57 |
| Absolute magnitude | +0.98 (0.92 – 1.05) |
| Distance | 102 ± 1 light-years (31.3 ± 0.3 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 29.9140 ± 0.1651 mas |
| Radial velocity | −0.47 ± 0.47 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: + 61.212 ± 0.162 mas/yr |
| Dec.: +2.412 ± 0.107 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 2.05 ± 0.29 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 40.4 ± 2.2 L☉ |
| Radius | 8.38 ± 0.58 R☉ |
| Temperature | 5,030 ± 160 K |
| Metallicity | −0.15 ± 0.10 dex |
| Age | 1.30 ± 1.04 billion years |
| Rotational velocity | 2.7 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 3.0 cgs |
| Constellation | Capricornus |
| Right ascension | 20h 18m 03.2555957142s |
| Declination | −12° 32′ 41.467632703″ |
| Names and designations | Algedi, Alpha2 Capricorni, Algiedi, Giedi, Algiedi Secunda, Secunda Giedi, 6 Capricorni, HD 192947, HR 7754, HIP 100064, SAO 163427, FK5 761, BD−12° 5685, GC 28200, GCRV 12666, GSC 05749-02530, JP11 3210, PPM 237217, PLX 4829.00, IRAS 20152-1242, 2MASS J20180324-1232418, UBV 17558, PMC 90-93 538, TYC 5749-2530-1, Gaia DR2 6880093650312745984, Gaia DR3 6880093650314169984, ADS 13645, IDS 20125-1251 A, CCDM J20181-1233A, WDS J20181-1233A,BC |