Botein, Delta Arietis (δ Ari), is a red clump giant located 165 light years away in the zodiac constellation of Aries. With an apparent magnitude of 4.349, it is the fifth brightest star in Aries. It appears in the same region of the sky as the Pleiades.
Star type
Botein is a red clump giant star of the spectral type K2 III. It is an evolved star that has undergone a helium flash and is now burning helium in its core. The star has 1.91 times the Sun’s mass and has expanded to a size of 10.42 solar radii. With an effective temperature of 4,810 K, it shines with around 45 solar luminosities.
The star is classified as a suspected variable. Its brightness has been reported to vary between magnitude 4.33 and 4.37.
Botein spins with a projected rotational velocity of 4.3 km/s. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +23 km/s.
Delta Arietis has been listed as member of the disputed Hyades Stream (Hyades moving group), a large group of stars that share a similar motion through space with the Hyades cluster (Melotte 25) in Taurus.

Botein (Delta Arietis), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Name
The name Botein (pronunciation: /ˈboʊtiːn/) comes from the Arabic Al Buṭayn (Al Buṭain), meaning “the little belly.” The word is the diminutive of Al Baṭn, “the belly.” This was the name of an old Arabic lunar mansion consisting of Botein, Epsilon Arietis, Pi Arietis, Zeta Arietis, and Rho3 Arietis. Delta Arietis was known as Botein (Al Buṭain), while the other four stars were called Al Buṭain I (Pi Arietis), Al Buṭain II (Rho3 Arietis), Al Buṭain III (Epsilon Arietis), and Al Buṭain IV (Zeta Arietis).
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) officially approved the name Botein for Delta Arietis on September 12, 2016.
Egyptian astronomer Al Achsasi A Mouakket designated Delta Arietis Nir al Botain in his Calendarium (c. 1650). The name was later translated into Latin as Lucida Ventris, “the brightest of the belly.”
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Botein was known as 天陰四 (Lóu Su sì), the Fourth Star of Yin Force. It formed the Yin Force (or Celestial Yin Force) asterism with Tau2 Arietis, Zeta Arietis, Tau1 Arietis, and 65 Arietis. The asterism was part of the larger Hairy Head mansion, which represented the body of the White Tiger.
Location
Botein lies in the eastern part of Aries, in the same region as the bright Pleiades cluster in Taurus. The star appears a little more than halfway between Aldebaran in Taurus and Mesarthim in Aries, close to the imaginary line extended from Almach in Andromeda through Bharani in Aries.
At declination +20°, Botein is visible from virtually anywhere for at least part of the year.
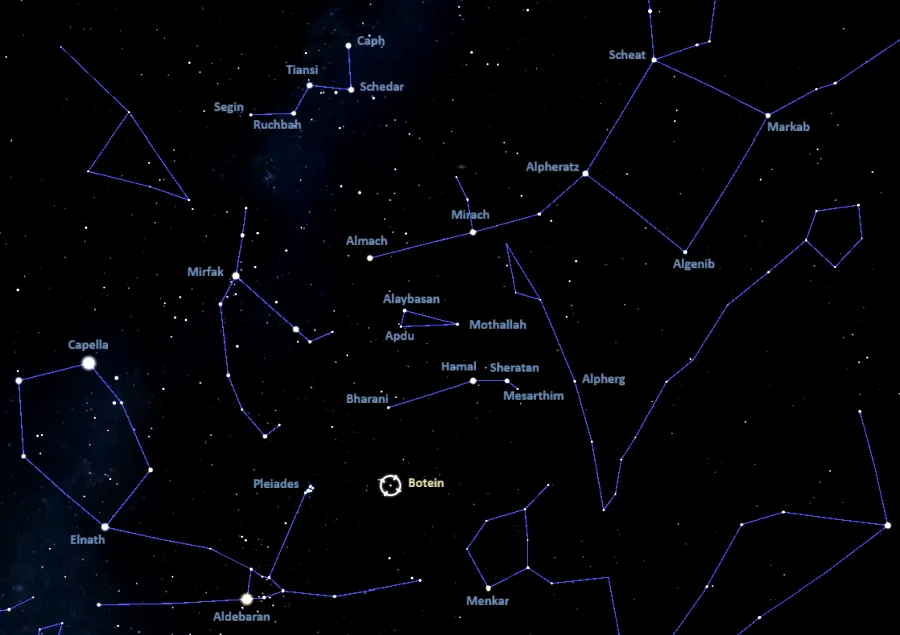
Botein location, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Botein is located in the constellation Aries. The Ram is one of the 48 ancient constellations, catalogued by the Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, the constellation is associated with Chrysomallos, the golden ram that rescued Phrixus and took him to Colchis. In Greek lore, Phrixus sacrificed the ram to Zeus and gave its fleece to King Aeëtes. The golden fleece was later stolen by Jason and the Argonauts with the help of Aeëtes’ daughter Medea.
Aries is the 39th largest constellation in the sky. It stretches across 441 square degrees north of the celestial equator. The constellation’s three bright stars – Hamal (Alpha Arietis), Sheratan (Beta Arietis), and Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis) – form a flat triangle just below the elongated constellation figure of Triangulum.
Hamal, the constellation’s lucida, is an orange giant with an apparent visual magnitude of 2.0, located 65.8 light-years away. It marks the forehead of the celestial Ram, while its neighbours Sheratan and Mesarthim form one of the Ram’s horns. Sheratan is a white main sequence star in a binary system and Mesarthim is a variable A-type star in a double or triple star system.
Other notable stars in Aries include the hot blue star Bharani (41 Arietis), the K-type giants Lilii Borea (39 Arietis) and HD 20644, the chemically peculiar variable star SX Arietis, the yellow dwarf HIP 14810 with three orbiting planets, and the nearby red dwarf known as Teegarden’s Star with a system of at least three planets, two of which are potentially habitable.
Aries hosts several notable deep sky objects, including the Fiddlehead Galaxy (NGC 772), the spiral galaxies NGC 972, NGC 691, NGC 695 and IC 167, the interacting galaxies UGC 2369 and Arp 276, and the elliptical galaxies NGC 680, NGC 770, and NGC 821.
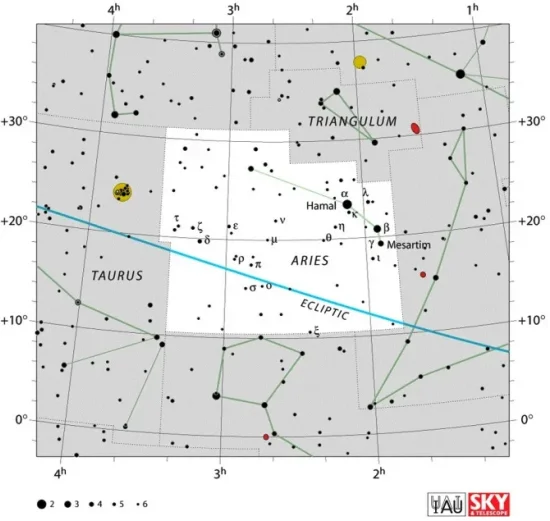
Aries constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects in Aries is during the month of December, when the celestial Ram climbs higher in the sky in the early evening. The entire constellation can be seen from locations north of the latitude 60° S.
The 10 brightest stars in Aries are Hamal (Alpha Ari, mag. 2.00), Sheratan (Beta Ari, mag. 2.66), Bharani (41 Ari, mag. 3.63), Mesarthim (Gamma Ari, mag. 3.86), Botein (Delta Ari, mag. 4.349), HD 20644 (mag. 4.47), Lilii Borea (39 Ari, mag. 4.514), 35 Arietis (mag. 4.64), Lambda Arietis (mag. 4.79), and Zeta Arietis (mag. 4.89).
Botein – Delta Arietis
| Spectral class | K2 III |
| Variable type | Suspected |
| U-B colour index | +0.914 |
| B-V colour index | +1.035 |
| R-I colour index | +0.51 |
| Apparent magnitude | 4.349 |
| Absolute magnitude | +0.77 |
| Distance | 165 ± 1 light-years (50.6 ± 0.4 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 19.7731 ± 0.1592 mas |
| Radial velocity | +23.0056 ± 0.0259 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: +153.871 ± 0.262 mas/yr |
| Dec.: –5.586 ± 0.150 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 1.91 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 45 ± 6 L☉ |
| Radius | 10.42 ± 0.97 R☉ |
| Temperature | 4,810 K |
| Metallicity | -0.03 dex |
| Rotational velocity | 4.3 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 2.93 cgs |
| Constellation | Aries |
| Right ascension | 03h 11m 37.7665678572s |
| Declination | +19° 43′ 36.023197055″ |
| Names and designations | Botein, Delta Arietis, Delta Ari, δ Arietis, δ Ari, 57 Arietis, 57 Ari, HD 19787, HR 951, HIP 14838, SAO 93328, FK5 114, BD+19°477, AG+19 243, GC 3805, GCRV 1756, PLX 657.00, PPM 118897, AP J03113776+1943360, SKY# 4775, USNO-B1.0 1097-00034579, TD1 1958, ASCC 835826, IRC +20054, TIC 113875184, GEN# +1.00019787, JP11 756, CSV 100261, GSC 01228-02019, LSPM J0311+1943, N30 648, NSV 1066, PMC 90-93 82, ROT 425, SRS 30114, UBV 3069, UBV M 9373, WEB 2865, YZ 19 848, [HFE83] 204, IRAS 03087+1932, 2MASS J03113776+1943360, TYC 1228-2019-1, Gaia DR2 60248877811328768, Gaia DR3 60248877811546112 |