Aldulfin, Epsilon Delphini (ε Del), is a hot blue giant star located approximately 330 light-years away in the constellation of Delphinus. It marks the tail of the celestial Dolphin. With an apparent magnitude of 4.03, it is the third brightest star in the constellation, after Rotanev (Beta Delphini) and Sualocin (Alpha Delphini).
Star type
Aldulfin is a blue giant of the spectral type B6 III. The massive star has a radius 4.6 times that of the Sun and an energy output of 676 solar luminosities. It has an effective temperature of 13,614 K and spins with a projected rotational velocity of around 52 km/s. The evolved star has an estimated age of 220 million years, which is only a fraction of the Sun’s age (4.6 billion years).
Aldulfin is a variable star. Its brightness has been reported to occasionally increase to magnitude 3.95.
The brightness of Epsilon Delphini is dimmed by interstellar dust by an extinction factor of 0.11. The star is moving in the direction of the Sun at 19 km/s.
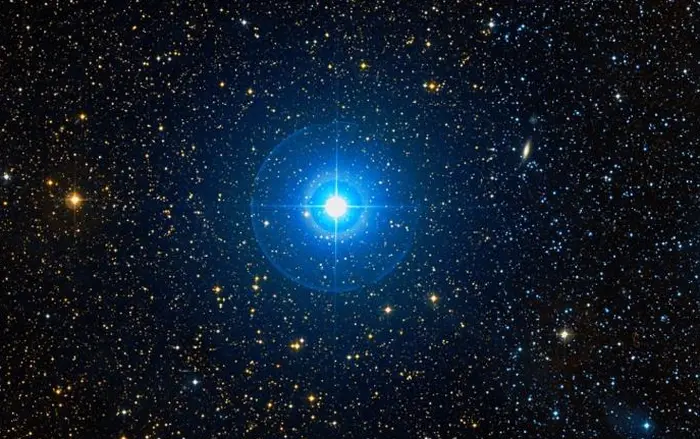

Aldulfin (Epsilon Delphini), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Name
The name Aldulfin (pronunciation: /ælˈdʌlfən/) comes from the Arabic ðanab ad-dulfīn (Dzaneb al Delphin), meaning “the dolphin’s tail.” The name appeared in the 17th century Egyptian astronomer Al Achsasi al Mouakket’s Calendarium. It was later translated into Latin as Cauda Delphini.
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) approved the name Aldulfin for Epsilon Delphini on September 5, 2017.
Aldulfin was traditionally also known as Deneb Dulfim, meaning “the tail of the Dolphin.” It was one of the several relatively bright Denebs in the sky, along with Deneb in the constellation Cygnus (the Swan), Deneb Algedi in Capricornus, Aldhanab in Grus (the Crane), and Denebola in Leo. Other stars that were historically called Deneb include Deneb Kaitos (Beta Ceti) in Cetus (the Sea Monster) and Deneb Okab (Zeta Aquilae) in Aquila. These stars are now formally known as Diphda (Beta Ceti) and Okab (Zeta Aquilae). Most of these stars (all except Aldhanab) mark the tails of the animals represented by their host constellations.
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Aldhanab was known as 敗瓜一 (Bài Guā yī), the First Star of Rotten Gourd. It formed an asterism called Rotten Gourd with Eta Delphini, Theta Delphini, Iota Delphini, and Kappa Delphini. The asterism was part of the larger Girl mansion, one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise. The name Pae Chaou comes from the star’s Chinese name.
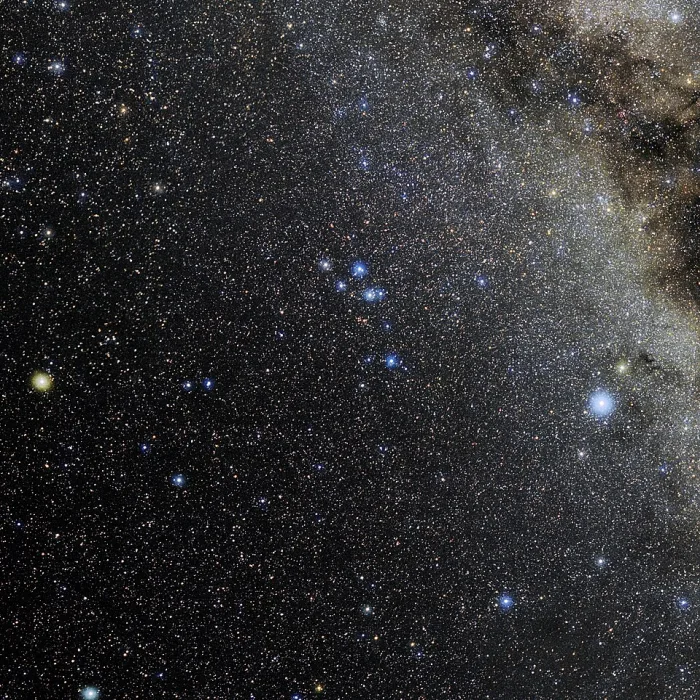

Photo of the constellation Delphinus produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer. Image credit: E. Slawik/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani (CC BY 4.0)
Location
Aldulfin is easy to find because it is part of the distinctive constellation figure of the Dolphin. It marks the Dolphin’s tail, while Rotanev (Beta Delphini), Sualocin (Alpha Delphini), Gamma Delphini and Delta Delphini outline its body.
Aldulfin lies close to the imaginary line connecting Altair, the brightest star in Aquila, and Enif, the luminary of Pegasus. The faint lenticular galaxy LEDA 64916 (UGC 11587) appears in the same field of view.
At declinaton +11°, Epsilon Delphini is visible from virtually any location for at least part of the year.
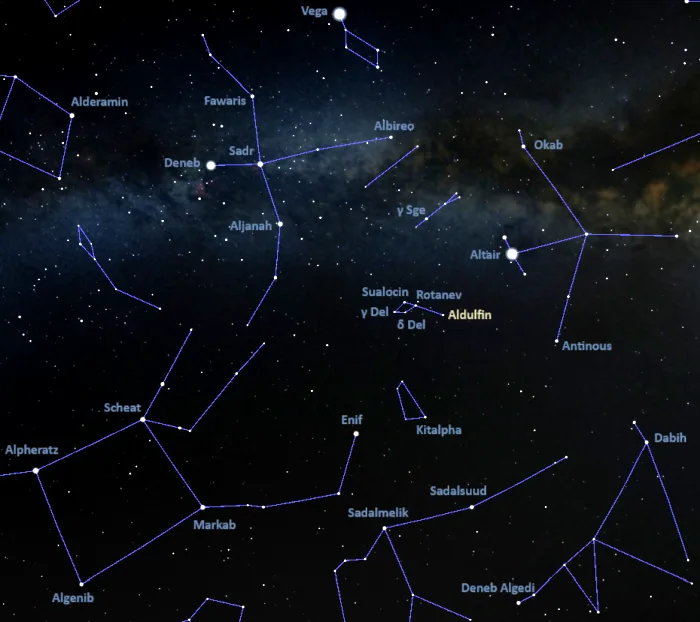
Epsilon Delphini location, image credit: Stellarium
Constellation
Aldulfin is located in the constellation Delphinus. Associated with Poseidon’s messenger Delphinus and with the tale of the Greek poet Arion, who was saved by dolphins at sea, the Dolphin is one of the ancient constellations. It was catalogued by the Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century AD. Stretching across only 189 square degrees just north of the celestial equator, it is the 69th constellation in size.
The brightest star in Delphinus, Rotanev (Beta Delphini), is a yellow-white giant with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.617. It lies 101 light years away.
Other notable stars in the constellation include the blue subgiant Sualocin (Alpha Delphini), the binary systems Gamma and Kappa Delphini, the orange supergiant Theta Delphini, the Delta Scuti star Delta Delphini, the classical nova V339 Delphini (Nova Delphini 2013), the yellow symbiotic star He 2-467, the white subgiants Eta and Iota Delphini, and the yellow giant Musica (18 Delphini), which hosts an extrasolar planet, named Arion.
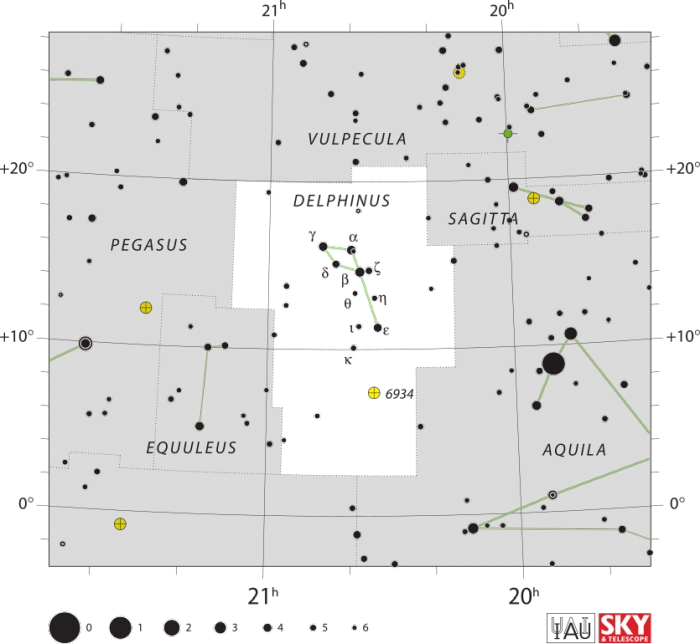
Delphinus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Deep sky objects in the constellation include the planetary nebulae NGC 6905 (the Blue Flash Nebula) and NGC 6891, the globular clusters NGC 6934 (C47) and NGC 7006 (C42), and the spiral galaxies NGC 7003, NGC 6956, and NGC 7025.
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects in Delphinus is during the month of September, when the constellation climbs high above the horizon in the early evening. The entire constellation can be seen from locations north of the latitude 69° S. It lies close enough to the celestial equator to be visible from any inhabited location on Earth.
The 10 brightest stars in Delphinus are Rotanev (Beta Del, mag. 3.617), Sualocin (Alpha Delphini, mag. 3.777), Aldulfin (Epsilon Delphini, mag. 4.03), Gamma Delphini (mag. 4.360), Delta Delphini (mag. 4.43), Zeta Delphini (mag. 4.647), Rho Aquilae (mag. 4.94), Kappa Delphini (mag. 5.05), 17 Delphini (mag. 5.18), and Eta Delphini (mag. 5.38).
Aldulfin – Epsilon Delphini
| Spectral class | B6 III or B6 IV |
| Variable type | Suspected |
| U-B colour index | −0.46 |
| B-V colour index | −0.13 |
| Apparent magnitude | 4.03 (3.95 – 4.05) |
| Absolute magnitude | −0.06 |
| Distance | 330 ± 7 light-years (101 ± 2 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 8.9149 ± 0.1993 mas |
| Radial velocity | −19.4 ± 0.7 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: +10.915 ± 0.212 mas/yr |
| Dec.: -19.606 ± 0.161 mas/yr | |
| Luminosity | 676 L☉ |
| Radius | 4.6 R☉ |
| Temperature | 13,614 ± 15 K |
| Metallicity | +0.08 ± 0.10 dex |
| Age | 220 million years |
| Rotational velocity | 52 ± 4 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 3.71 ± 0.09 cgs |
| Constellation | Delphinus |
| Right ascension | 20h 33m 12.7728639045s |
| Declination | +11° 18′ 11.758994803″ |
| Names and designations | Aldulfin, Deneb Dulfim, Epsilon Delphini, Epsilon Del, ε Delphini, ε Del, 2 Delphini, 2 Del, HD 195810, HR 7852, HIP 191421, SAO 106230, BD+10°4321, AG+11 2513, FK5 768, SKY# 38903, GC 28593, GCRV 12848, ALS 16377, PPM 138578, GEN# +1.00195810, PLX 4888.00, CEL 5102, JP11 3251, N30 4539, PMC 90-93 542, 2MASS J20331277+1118118, ROT 2995, SRS 30768, SV* SVS 10, TIC 374799948, TD1 26903, TYC 1096-1684-1, UBV 17820, UBV M 24944, uvby98 100195810, WEB 18323, YZ 11 7990, Gaia DR2 1755320049742345472, Gaia DR3 1755320049747788160 |