Diadem, Alpha Comae Berenices (α Com), is a binary star located 58.1 light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. With a combined apparent magnitude of 4.29 – 4.35, it is the second brightest point of light in Coma Berenices, after Beta Comae Berenices. The star system appears near the bright globular clusters Messier 53 and NGC 5053 in the sky.
Star system
Alpha Comae Berenices is a binary star system composed of two yellow-white main sequence stars of the spectral type F5V. Some sources give the spectral classes F5V and F6V for the two components. The stars are separated by 0.67144 arcseconds in the sky and have an orbital period of 25.8696 years. Both stars are slightly more massive and luminous than the Sun. Individually, they shine at magnitudes 4.85 and 5.53.
Alpha Comae Berenices A has a mass of 1.237 solar masses and an effective temperature of 6,365 kelvin. It is 1.72 times more luminous than the Sun.
The companion, Alpha Comae Berenices B, has a mass of 1.87 solar masses and a luminosity 1.75 times that of the Sun. It has a surface temperature of 6,378 K.
The physical separation between Alpha Comae Berenices A and B is around 10 astronomical units (AU), comparable to the distance from the Sun to Saturn.
The two components have an optical companion at an angular separation of 89 arcseconds. The companion has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.2 and is catalogue as CCDM J13100+1732C in the Catalog of Components of Double and Multiple Stars.
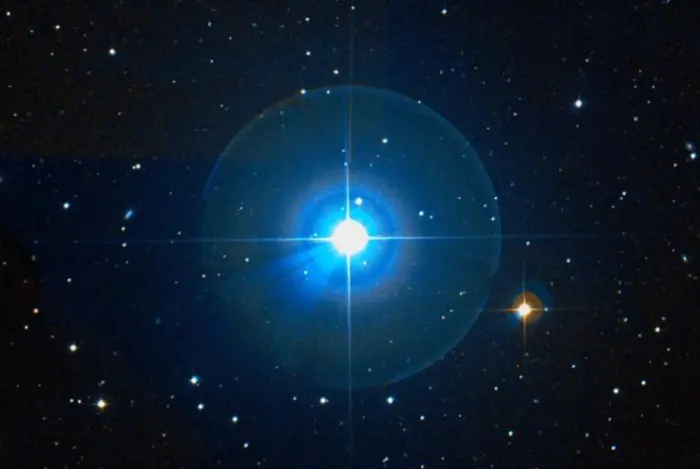

Diadem (Alpha Comae Berenices), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Name
The name Diadem refers to the wreath of jewels worn by the Queen Berenice II Euergetis of Egypt, represented by the constellation Coma Berenices (Berenice’s Hair).
The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) on February 1, 2017. It formally applies only to the primary component in the system, Alpha Comae Berenices A.
Alpha Comae Berenices was traditionally also known as Al Dafirah, derived from the Arabic đ̧-đ̧afīrah, meaning “the braid.”
In traditional Chinese astronomy, Diadem was known as 太微左垣五 (Tài Wēi Zuǒ Yuán wǔ), the Fifth Star of Left Wall of Supreme Palace Enclosure. It formed the asterism called Left Wall of Supreme Palace Enclosure with Zaniah (Eta Virginis), Porrima (Gamma Virginis), Minelauva (Delta Virginis), and Vindemiatrix (Epsilon Virginis) in the constellation Virgo. Diadem represented the First Eastern General (東上將, Dōngshǎngjiāng).
Location
Diadem is relatively easy to find but since it is not particularly bright, it can be a difficult target from areas with too much light pollution. The star system appears in the southeastern part of Coma Berenices, about 10.4 degrees south of the slightly brighter Beta Comae Berenices.
Diadem lies almost halfway between the bright Arcturus in the constellation Boötes and Denebola in Leo. Seen from northern latitudes, the star lies just above the top left side of the crooked Y of Virgo, marked by Vindemiatrix. The left side of the Y points towards Diadem.
Diadem lies near the centre of the Diamond of Virgo, a large seasonal asterism formed by Arcturus and Denebola with Cor Caroli in Canes Venatici and Spica in Virgo. Arcturus and Spica can be found by following the curved line of the Big Dipper’s handle. The constellation figure of Leo can be found by extending a line from Megrez through Phecda, the inner stars of the Big Dipper’s bowl. Denebola marks the Lion’s tail, and Cor Caroli is the brightest star between Alkaid at the tip of the Great Bear’s tail and Denebola.
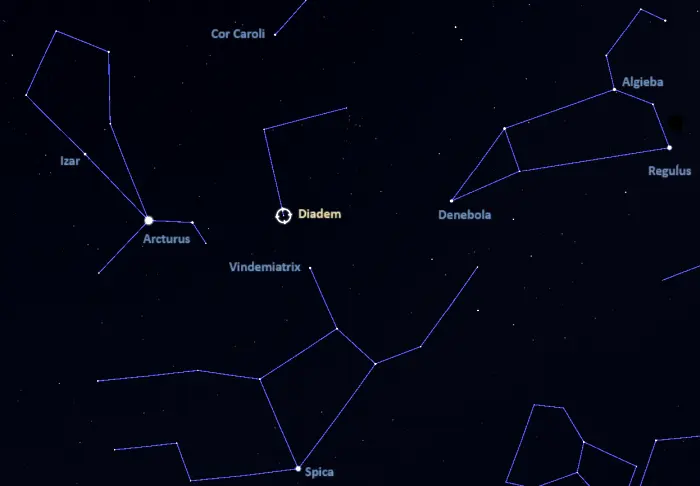
The location of Diadem (Alpha Comae Berenices), image: Stellarium
Diadem appears just west of the globular clusters Messier 53 and NGC 5053. The brighter M53 has an apparent magnitude of 7.6 and can be spotted in binoculars. NGC 5053 is considerably fainter. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.96. The two old star clusters are connected by a tidal bridge and may have interacted in the past. Both are over 12 billion years old.
At declination 17° 32’, Diadem is close enough to the celestial equator to be visible from both hemispheres for at least part of the year.

Diadem, Messier 53 and NGC 5053, image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Constellation
Diadem is located in the constellation of Coma Berenices (Berenice’s Hair). Coma Berenices represents the hair of Queen Berenice II of Egypt. It is the only modern constellation associated with a historical figure. Berenice cut off her long hair and placed it in a temple in Alexandria as an offering for the safe return of her husband. The constellation was introduced as asterism by Conon of Samos, the court astronomer of King Ptolemy III Euergetes, to commemorate the king’s consort in 245 BC.
The ancient Greek polymath Eratosthenes called the asterism “Berenice’s Hair,” but considered it to be part of Leo. Coma Berenices represented the tuft of hair at the tip of the Lion’s tail. German astronomer Casper Vopel is credited for making it a separate constellation in 1536.
Coma Berenices is the 42nd largest constellation in the sky. It stretches across 386 square degrees of the sky north of the celestial equator. It does not host any exceptionally bright stars. The constellation’s lucida, Beta Comae Berenices, is a Sun-like star that shines at magnitude 4.26 from a distance of 29.95 light years.
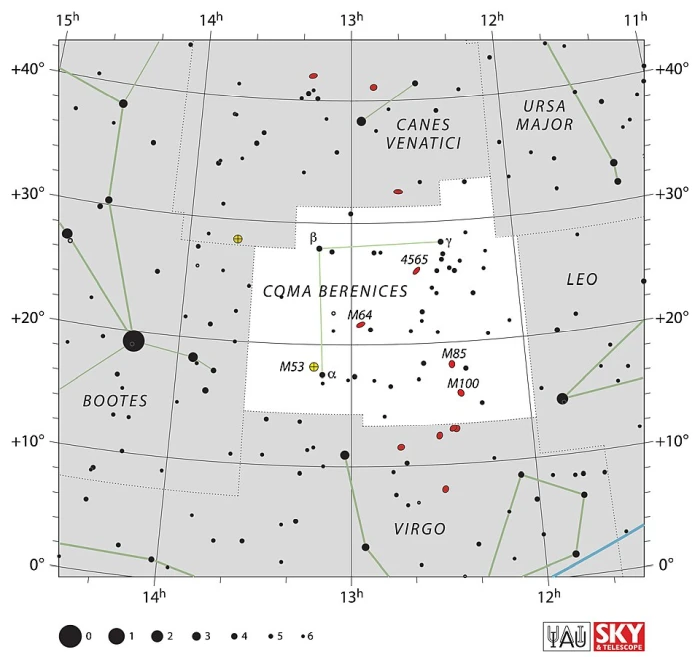
Coma Berenices constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Other notable stars in Coma Berenices include the orange giant Gamma Comae Berenices, the binary star 11 Comae Berenices, the red giant 36 Comae Berenices, the variable G-type giant 37 Comae Berenices, the binary system 12 Comae Berenices (the brightest member of the Coma Star Cluster), the orange dwarf HD 110067 with six orbiting planets, and the yellow giant 31 Comae Berenices, sometimes called Polaris Galacticum Borealis (north galactic pole star).
Coma Berenices is known for its many galaxies and the bright, large Coma Star Cluster (Melotte 111), an open cluster visible without binoculars. The cluster occupies 7.5 degrees of the sky in the northwestern part of the constellation. With an apparent magnitude of 1.8, it is one of the brightest open clusters in the sky, along with the Pleiades and Hyades in Taurus and the Alpha Persei Cluster in Perseus.
Coma Berenices also hosts several relatively bright globular clusters, including Messier 53, NGC 5053, and NGC 4147.
Bright galaxies in the constellation include the Black Eye Galaxy (Messier 64), the edge-on Needle Galaxy (NGC 4565), the Umbrella Galaxy (NGC 4651), the Dusty Spiral Galaxy (NGC 4414), and the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4314.
Coma Berenices contains the Coma Supercluster of galaxies, which includes the Coma Cluster (Abell 1656) and the Leo Cluster (Abell 1367). The brightest members of the Coma Cluster are the supergiant elliptical galaxies NGC 4874 and NGC 4889. Other members include the interacting spiral galaxies known as the Mice Galaxies (NGC 4676) and the spiral galaxies NGC 4921 and NGC 4911.
Coma Berenices also hosts a portion of the Virgo Cluster, including the Messier galaxies Messier 85, Messier 88, Messier 91, Messier 98, Messier 99 (the Coma Pinwheel Galaxy), and Messier 100 (the Mirror Galaxy).
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects in Coma Berenices is during the month of May, when the constellation appears higher above the horizon in the early evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations north of the latitude 70° S.
The 10 brightest stars in Coma Berenices are Beta Comae Berenices (mag. 4.26), Diadem (Alpha Com, mag. 4.29 – 4.35), Gamma Comae Berenices (mag. 4.36), 11 Comae Berenices (mag. 4.72), 36 Comae Berenices (mag. 4.76), 12 Comae Berenices (mag. 4.80), Phyllon Kissinou (23 Com, mag. 4.80), 41 Comae Berenices (mag. 4.80), 35 Comae Berenices (mag. 4.93), and 37 Comae Berenices (mag. 4.88).
Diadem – Alpha Comae Berenices
| Spectral class | F5V + F5V (or F5V + F6V) |
| U-B colour index | −0.06 |
| B-V colour index | 0.45 |
| V-R colour index | 0.2 |
| R-I colour index | 0.2 |
| Apparent magnitude | 4.29 – 4.35 |
| Absolute magnitude | 3.82 |
| Distance | 58.1 ± 0.9 light-years (17.8 ± 0.3 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 56.10 ± 0.89 mas |
| Radial velocity | -18.826 ± 0.0016 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: −433.13 ± 0.70 mas/yr |
| Dec.: 141.24 ± 0.51 mas/yr | |
| Constellation | Coma Berenices |
| Right ascension | 13h 09m 59.28520s |
| Declination | +17° 31′ 46.0389″ |
| Names and designations | Diadem, Alpha Comae Berenices, Alpha Com, α Comae Berenices, α Com, 42 Comae Berenices, 42 Com, HIP 64241, SAO 100443, PPM 129630, Gliese 501, GJ 501, BD+18 2697, AG+17 1350, GC 17833, GCRV 7832, GCRV 63887, LTT 13802, NLTT 33105, WEB 11357, AAVSO 1305+18, SKY# 24360, NSV 6116, AKARI-IRC-V1 J1309590+173147, ASCC 868407, Ci 20 762, CNS5 3241, CSI+18 2697 1, CSV 102722, PLX 3006.00, RBS 1225, GEN# +1.00114378, LSPM J1309+1731, UBV 11895, RE J130959+173150, ROT 1938, RX J1309.9+1731, RX J1310.0+1731, 1RXS J130959.3+173136, RX J1309.9+1731 1, YZ 17 4848, EUVE J1310+17.5, 2EUVE J1310+17.5, uvby98 100114378, TD1 16671, TIC 138128530, WISE J130958.97+173146.5, WISEA J130958.98+173147.5, USNO-B1.0 1075-00257793, IRAS 13075+1747, IRAS F13075+1747, 2MASS J13095936+1731456, Gaia DR3 3937881211045638400, STF 1728, STF 1728AB, ADS 8804, ADS 8804 AB, CCDM J13100+1732, CCDM J13100+1732AB, IDS 13051+1803 AB, WDS 13100+1732, WDS J13100+1732AB |
Alpha Comae Berenices A
| Spectral class | F5V |
| Apparent magnitude | 4.85 |
| Mass | 1.237 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.72 L☉ |
| Temperature | 6,365 K |
| Metallicity | -0.23 dex |
| Surface gravity | 4.19 |
| Names and designations | Diadem, Alpha Comae Berenices A, Alpha Com A, α Comae Berenices A, α Com A, 42 Comae Berenices A, 42 Com A, HD 114378, HR 4968, BD+18 2697A, GJ 501 A, CSI+18 2697 3, TYC 1454-1134-1, STF 1728A, ADS 8804 A, CCDM J13100+1732A, IDS 13051+1803 A, WDS J13100+1732A |
Alpha Comae Berenices B
| Spectral class | F5V or F6V |
| Apparent magnitude | 5.53 |
| Mass | 1.087 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 1.75 L☉ |
| Temperature | 6,378 K |
| Names and designations | Alpha Comae Berenices B, Alpha Com B, α Comae Berenices B, α Com B, 42 Comae Berenices B, 42 Com B, HD 114379, HR 4969, BD+18 2697B, GJ 501 B, TYC 1454-1134-2, CSI+18 2697 4, ADS 8804 B, CCDM J13100+1732B, IDS 13051+1803 B, WDS J13100+1732B |