Aldhibah, Zeta Draconis (ζ Dra), is a binary star system located approximately 330 light-years away in the constellation Draco. With an apparent magnitude of 3.17, it is the fifth brightest star in Draco. It appears in the region between the Dragon’s head and the bowl of the Little Dipper in Ursa Minor.
Star system
Zeta Draconis is a binary star composed of Zeta Draconis A (formally known as Aldhibah) and Zeta Draconis B.
The primary component, Zeta Draconis A, is an evolved, massive, blue giant star of the spectral type B8 III. It has a mass 5.94 times that of the Sun and a radius 6.19 times the Sun’s. With an effective temperature of around 15,000 K, it is 883 times more luminous than the Sun. The star is a fast spinner, with a projected rotational velocity of 55 km/s.
The companion, Zeta Draconis B, is also more massive than the Sun. It has an estimated mass of 3.645 solar masses.
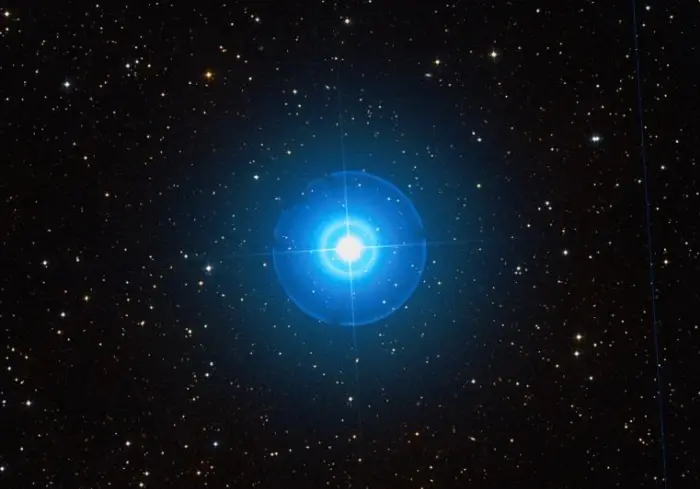

Aldhibah (Zeta Draconis), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Facts
Shining at magnitude 3.17, Zeta Draconis is the fifth brightest point of light in the constellation Draco, after Eltanin, Athebyne, Rastaban, and Altais. Aldhibah is, on average, the 203rd brightest star in the sky. It is about as bright as Pipit (Nu Puppis) in the constellation Puppis, Theta Ursae Majoris in Ursa Major, Phi Sagittarii in Sagittarius, and Haedus (Eta Aurigae) in Auriga.
Zeta Draconis is the north pole star of the planet Jupiter.
The star can be used to find the north ecliptic pole, which lies roughly halfway between Zeta and Delta Draconis (Altais). The north ecliptic pole almost coincides with the southern celestial pole of the planet Venus.
Name
The name Aldhibah (pronunciation: /ælˈdaɪbə/) comes from the Arabic al-dhiʼb, meaning “the wolf” or “the hyena.” It has a similar etymology to Athebyne, which comes from the dual form al-dhiʼbayn, “the (two) wolves.” Eta and Zeta Draconis were traditionally called Al Dhibain Prior and Al Dhibain Posterior.
In Arabic astronomy, Aldhibah and Athebyne (Zeta and Eta Draconis) represented two wolves or hyenas stalking a camel’s foal. The foal was protected by the Mother Camels, represented by an asterism of the same name. The asterism was formed by Eltanin, Rastaban, Grumium, Kuma and Alrakis, while the foal was represented by the fainter Alruba (HD 161693).
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) officially approved the name Aldhibah for Zeta Draconis on September 5, 2017. The name formally applies only to the primary component, Zeta Draconis A, but was historically used for the whole star system.
Zeta Draconis was also known as Nodus Tertius (Nodus III), meaning the Third Knot. The name referred to the third loop in the Dragon’s body and tail. The other nodes are Grumium (Nodus I), Altais (Nodus II), and either Theta Draconis or Edasich (Nodus IV).
In Hindu astronomy, Aldhibah was associated with Tara, a celestial goddess who personified the stars in the sky. In Hindu lore, Tara was married to Brihaspati, a god associated with fire and the planet Jupiter. She was abducted by Lord Chandra, the god of the Moon, with whom she bore a son, Lord Budha (Mercury).
In Arabic astronomy, Eta and Zeta Draconis were sometimes called Al ‘Auhakan, “the two black bulls (or ravens).”
In old Chinese astronomy Aldhibah was known as 紫微左垣四 (Zǐ Wēi Zuǒ Yuán sì), the Fourth Star of Left Wall of Purple Forbidden Enclosure. It formed the Left Wall asterism with Edasich (Iota Draconis), Theta Draconis, Athebyne (Eta Draconis), Upsilon Draconis, 73 Draconis, Pi Cephei, and 23 Cassiopeiae. The asterism represented eight guardian stars and was part of the larger Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which represented the imperial palace. Zeta Draconis represented 上弼 (Shǎngbì), the First Minister (or the Higher Minister).
Location
Aldhibah and Athebyne appear in the area between the head of the celestial Dragon, outlined by Eltanin, Rastaban, Grumium and Kuma, and the Little Dipper’s bowl. Aldhibah lies close to the midpoint of the imaginary line connecting Kochab in Ursa Minor and Grumium in the Dragon’s head. The brighter Athebyne can be found by following the line formed by the Guardians of the Pole – Kochab and Pherkad – in the direction of the Keystone asterism in Hercules.
At declination + 65° 43’, Aldhibah is best seen from the northern hemisphere. It never rises for observers south of the latitude 24° S and stays close to the northern horizon from the southern tropical latitudes.
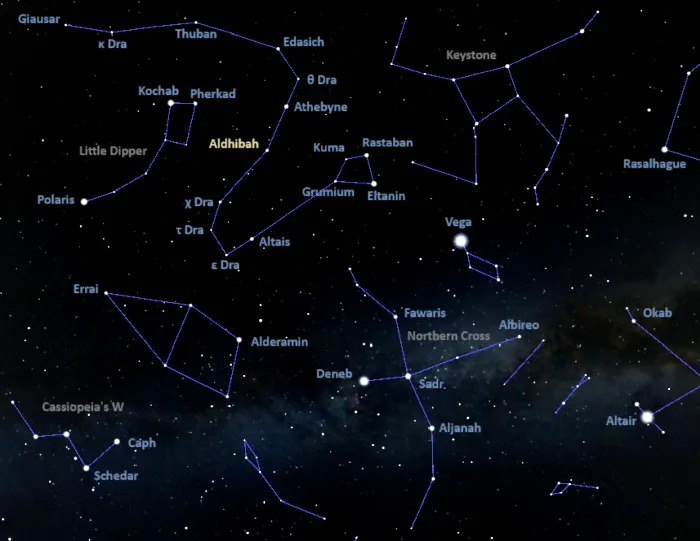
Location of Aldhibah (Zeta Draconis), image: Stellarium
Constellation
Aldhibah is located in the northern constellation of Draco. The celestial Dragon is one of the Greek constellations, catalogued by Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, the constellation is associated with the dragon Ladon, tasked with guarding the gardens of the Hesperides.
Draco is the eighth largest constellation in the sky, stretching across an area of 1,083 square degrees. The constellation’s brightest star, the K-type giant Eltanin, shines at magnitude 2.23 from a distance of 154.3 light-years.
Other notable stars in Draco include the white subgiant Thuban (Alpha Draconis), the yellow giants Athebyne (Eta Draconis), Altais (Delta Draconis) and Omicron Draconis, the yellow bright giant or supergiant Rastaban (Beta Draconis), the orange giant Edasich (Iota Draconis), the blue giant Kappa Draconis, and the multiple star system Mu Draconis (Alrakis).
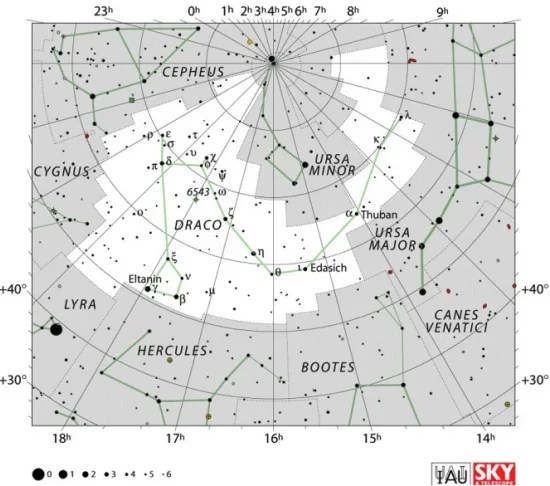
Draco constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
Deep sky objects in Draco include the Cat’s Eye Nebula (NGC 6543), the Draco Dwarf galaxy, the Spindle Galaxy (Messier 102, NGC 5866), the Tadpole Galaxy (Arp 188), the Splinter Galaxy (NGC 5907), the Draco Trio (NGC 5981, NGC 5982 and NGC 5985), and the Dolphin Galaxy (NGC 6670).
The best time of the year to observe the stars and deep sky objects of Draco is during the month of July, when the constellation appears higher in the sky in the early evening. The entire constellation is visible from locations north of the latitude 15° S. It is circumpolar for observers in the northern hemisphere.
The 10 brightest stars in Draco are Eltanin (Gamma Dra, mag. 2.23), Athebyne (Eta Dra, mag. 2.73), Rastaban (Beta Dra, mag. 2.79), Altais (Delta Dra, mag. 3.07), Aldhibah (Zeta Dra, mag. 3.17), Edasich (Iota Dra, mag. 3.29), Chi Draconis (mag. 3.57), Thuban (Alpha Dra, mag. 3.6452), Grumium (Xi Dra, mag. 3.75), and Giausar (Lambda Dra, mag. 3.85).
Aldhibah – Zeta Draconis
| Spectral class | B8 III |
| U-B colour index | -0.43 |
| B-V colour index | -0.11 |
| Apparent magnitude | 3.17 |
| Absolute magnitude | -1.88 |
| Distance | 330 ± 10 light-years (101 ± 4 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 7.8274 ± 0.5476 mas |
| Radial velocity | -17.70 ± 0.3 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: -16.550 ± 0.666 mas/yr |
| Dec.: +32.757 ± 0.531 mas/yr | |
| Mass (ζ Dra A, ζ Dra B) | 5.940 ± 1.134 M☉, 3.645 ± 0.770 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 883 L☉ |
| Radius | 6.19 ± 0.49 R☉ |
| Temperature | 15,000 ± 800 K |
| Metallicity | -0.95 dex |
| Rotational velocity | 55 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 4.24 cgs |
| Constellation | Draco |
| Right ascension | 17h 08m 47.1877295740s |
| Declination | +65° 42′ 52.723177105″ |
| Names and designations | Aldhibah, Zeta Draconis, Zeta Dra, ζ Draconis, ζ Dra, 22 Draconis, 22 Dra, HD 155763, HR 6396, HIP 83895, SAO 17365, FK5 639, BD+65 1170, AG+65 806, ALS 16385, PPM 20234, HGAM 662, GC 23182, GCRV 9910, WEB 14179, PLX 3905.00, SKY# 30908, JP11 2824, N30 3833, TD1 20105, GEN# +1.00155763, GSC 04210-01048, ROT 2421, PMC 90-93 455, UBV 14549, UBV M 21988, IRAS 17086+6546, 2MASS J17084719+6542528, TYC 4210-1048-1, Gaia DR2 1632499034644070528, Gaia DR3 1632499034644723968, TIC 307986093, WDS 17088+6543 |