Alshat, Nu Capricorni (ν Cap), is a hot blue star located approximately 268 light-years away in the constellation Capricornus. With an apparent magnitude of 4.76, it is visible to the unaided eye. It appears in the horns of the celestial Sea Goat, near the brighter Algedi and Dabih.
Star type
Alshat is a hot blue main sequence star or subgiant with the spectral type B9.5 V or B9 IV. The star is either still fusing hydrogen in its core or coming to the end of its main sequence lifetime after having exhausted its supply of hydrogen fuel. It has a projected rotational velocity of 24 km/s, which is fairly slow for a B-type star.
Nu Capricorni has 2.37 times the Sun’s mass and a radius of around 3.04 solar radii. With an effective temperature of 10,200 K, it is around 89 times more luminous than the Sun. It is much younger than our host star, with an estimated age of only 115 million years.
In spite of being much younger, hotter and more massive, Alshat has a very similar composition to the Sun. The star’s nearly solar abundances were reported by Adelman in 1991 and confirmed by Monier in 2018.
Alshat has a visual companion, referred to as Nu Capricorni B. The optical companion has an apparent visual magnitude of 11.8 and is invisible to the unaided eye. It appears at a separation of 54.1 arcseconds from Nu Capricorni A. Based on the data obtained in Gaia Data Release 2 (GDR2), the faint star lies at a much greater distance and is not physically related to Alshat. It is part of a binary system that only appears in the same line-of-sight.
Nu Capricorni lies 6.6 degrees north of the ecliptic and be occasionally occulted by the Moon.
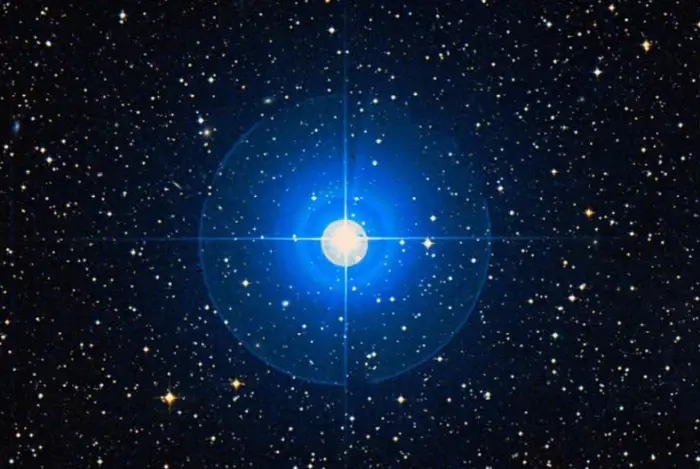

Alshat (Nu Capricorni), image credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 (CC BY 4.0)
Name
The name Alshat (pronunciation: /ˈælʃæt/) comes from the Arabic aš-šā[t] (Al Shat), meaning “the sheep.” The name is a reference to a sacrifice celebrated in old Arabic culture at the heliacal rising of Capricornus. The name of the nearby Beta Capricorni, Dabih (“the butcher”), has the same origin.
The International Astronomical Union’s (IAU) Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) approved the name Alshat for Nu Capricorni on June 30, 2017.
Location
Alshat is relatively easy to find. It appears less than a degree east-southeast of the brighter Algedi (Alpha2 Capricorni) and around 2 degrees north of Dabih (Beta Capricorni).
Algedi and Dabih can be found using the bright stars of Aquila (the Eagle). Altair, the brightest star in Aquila and the 12th brightest star in the sky, forms a conspicuous asterism called the Shaft of Aquila with Tarazed and Alshain, the two relatively bright stars flanking it. A line drawn through the Shaft of Aquila points in the direction of the right side of the V-shaped constellation figure of Capricornus. Dabih and Algedi are the brightest stars in this region of the sky, and the fainter Alshat appears right next to Algedi.
At declination −12° 45′, Alshat is visible from virtually anywhere for at least part of the year.
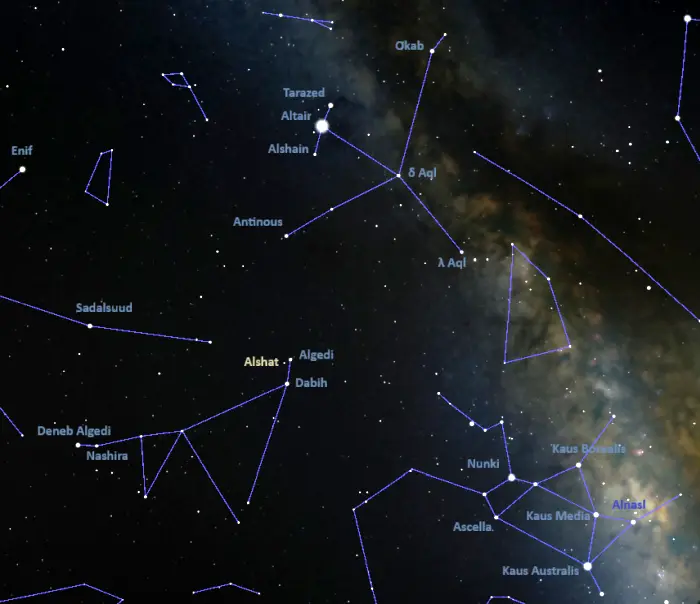
Alshat location, image: Stellarium
Constellation
Alshat is located in the constellation of Capricornus. It is the middle star in the celestial Sea Goat’s horns.
Capricornus is one of the 48 Greek constellations, catalogued by the Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy of Alexandria in his Almagest in the 2nd century CE. In Greek mythology, the Sea Goat constellation is linked with the goat Amalthea, who took care of Zeus when he was an infant. It is also associated with the forest god Pan.
The zodiac constellation does not stand out in the night sky. Its brightest star, Deneb Algedi (Delta Capricorni) is a white giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.81, located 38.70 light years away. Other stars in Capricornus are fainter than magnitude 3.0.
Notable stars in the constellation include the multiple star system Beta Capricorni (Dabih), the yellow supergiants Alpha1 Capricorni and Zeta Capricorni, the yellow giant or bright giant Algedi (Alpha2 Capricorni), the Am star Nashira (Gamma Capricorni), the orange giant Omega Capricorni, and the yellow giants Iota and Kappa Capricorni.
Capricornus does not have many bright deep sky objects. It is home to the globular clusters Messier 30 (M30) and Palomar 12, the elliptical galaxy NGC 7016, the compact galaxy group HCG 87, the interacting pair of lenticular galaxies NGC 7035 and NGC 7035A, and the spiral galaxies IC 1337, NGC 6907, and NGC 7019.
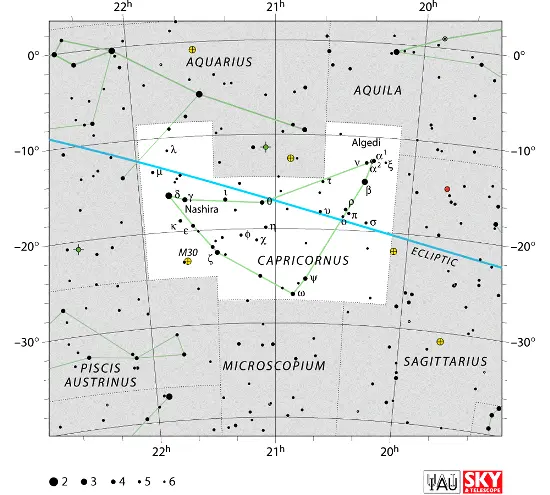
Capricornus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope magazine (Roger Sinnott & Rick Fienberg) (CC BY 3.0)
The best time of the year to see the stars and deep sky objects in Capricornus is during the month of September, when the constellation rises higher in the sky in the early evening. The entire constellation can be seen from locations south of the latitude 60° N.
The 10 brightest stars in Capricornus are Deneb Algedi (Delta Cap, mag. 2.81), Dabih (Beta Cap, mag. 3.05), Algedi (Alpha2 Cap, mag. 3.57), Nashira (Gamma Cap, mag. 3.67), Zeta Capricorni (mag. 3.77), Theta Capricorni (mag. 4.07), Omega Capricorni (mag. 4.11), Psi Capricorni (mag. 4.13), Iota Capricorni (mag. 4.296), and Alpha1 Capricorni (mag. 4.27).
Alshat – Nu Capricorni
| Spectral class | B9.5 V or B9 IV |
| U-B colour index | -0.11 |
| B-V colour index | -0.04 |
| Apparent magnitude | 4.76 |
| Absolute magnitude | +0.32 |
| Distance | 268 ± 4 light-years (82 ± 1 parsecs) |
| Parallax | 12.1737 ± 0.1597 mas |
| Radial velocity | -1.74 ± 0.23 km/s |
| Proper motion | RA: +14.130 ± 0.152 mas/yr |
| Dec.: −15.123 ± 0.103 mas/yr | |
| Mass | 2.37 M☉ |
| Luminosity | 89 ± 4 L☉ |
| Radius | 3.04 ± 0.08 R☉ |
| Temperature | 10,200 ± 220 K |
| Metallicity | −0.15 ± 0.04 dex |
| Age | 115 million years |
| Rotational velocity | 24 km/s |
| Surface gravity | 3.88 ± 0.08 cgs |
| Constellation | Capricornus |
| Right ascension | 20h 20m 39.8157949497s |
| Declination | −12° 45′ 32.690284207″ |
| Names and designations | Alshat, Nu Capricorni, Nu Cap, ν Capricorni, ν Cap, 8 Capricorni, 8 Cap, HD 193432, HR 7773, HIP 100310, SAO 163468, PPM 237275, PLX 4844.00, BD−13°5642, SKY# 38421, GC 28282, GCRV 12695, CSI-13 5642 1, GEN# +1.00193432, GSC 05749-02531, JP11 3222, ROT 2963, WISE J202039.82-124532.7, WISEA J202039.84-124532.7, LAM 5A, TD1 26510, RAVE J202039.8-124533, IRAS 20178-1255, 2MASS J20203982-1245328, TIC 114723106, TYC 5749-2531-1, UBV 17601, UBV M 24732, uvby98 100193432, YZC 11 7168, WEB 18091, Gaia DR2 6879844473485400576, Gaia DR3 6879844473490229888, ADS 13714 A, CCDM J20207-1246A, IDS 20151-1304 A, WDS J20207-1246A |